Ethernet for RP2350A in Minutes: WeAct RP2350A_V20 + WIZnet W5500 (SPI Hardwired TCP/IP)
Turn the WeAct RP2350A_V20 into a wired IoT node using WIZnet W5500 over SPI—fast bring-up, stable Ethernet, and simple socket-based networking.
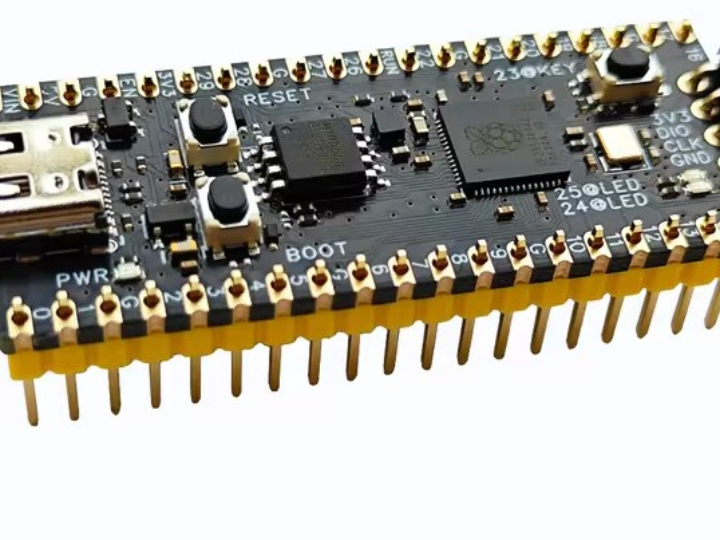
WeAct Studio - WeAct Studio RP2350A_V20
x 1
Introduction
Let’s start with what we’re building.
The WeAct RP2350A_V20 is a small, affordable board based on Raspberry Pi’s RP2350A, with a Pico 2-style layout and a USB-C port.
But out of the box, it’s still a microcontroller board—so if you want reliable wired networking, you’ll usually add an Ethernet controller.
That’s where WIZnet W5500 comes in.
WIZnet Product Integration
The networking block is simple and proven:
RP2350A_V20 ↔ SPI ↔ WIZnet W5500 ↔ Ethernet.
W5500 is a “hardwired TCP/IP” Ethernet controller, so you don’t need to implement the full network stack in your MCU firmware.
You mostly talk to it through socket-style APIs—and you’re online.
Technical Implementation
Here’s what we’re combining:
RP2350A_V20 (RP2350A SoC)
Dual-core Arm Cortex-M33 or dual-core Hazard3 RISC-V, up to 150 MHz
520 KB SRAM
4 MB or 16 MB QSPI flash options
USB Type-C (USB 1.1 host/device) for power and programming
2×20-pin headers, with lots of GPIO and PIO capability
WIZnet W5500
SPI interface, embedded MAC+PHY
8 hardware sockets and 32 KB internal buffer
Wiring (practical, “just works” approach)
Use any free SPI peripheral on RP2350A and wire:
RP2350A SCK → W5500 SCK
RP2350A MOSI → W5500 MOSI
RP2350A MISO → W5500 MISO
RP2350A CS → W5500 CS
RP2350A 3V3 → W5500 3V3
RP2350A GND → W5500 GND
Optional but recommended:
RP2350A GPIO → W5500 RST (reset control)
RP2350A GPIO → W5500 INT (interrupt-driven networking)
Note: pin names vary by board definition—so pick pins that match your SDK/Arduino pin map.
Reproduction Guide
Let’s bring it up step by step.
Flash a simple “SPI + Ethernet” test firmware to the RP2350A_V20.
Confirm SPI is alive (optional, but saves time).
Initialize W5500 with your MAC address.
Start DHCP and print the assigned IP.
Run a quick client test (HTTP GET) or a tiny TCP server.
If you see an IP address on the serial monitor, you’re done.
Core Features and Performance
Here’s what you get immediately:
Stable wired Ethernet for deployments where Wi‑Fi is a risk
Fast bring-up: socket-based networking on top of W5500
Good fit for real products: RP2350 security + W5500 proven Ethernet
Code Snippet
Here’s the core logic pattern: SPI init, W5500 init, then DHCP.
Once DHCP works, everything else is just your application protocol.
Applications and Extensions
A few real-world ways to use this combo:
Industrial sensors: reliable Ethernet + MCU simplicity
Building automation: long cable runs, centralized switching
Networked controllers: Modbus/TCP, simple TCP bridges, telemetry
Tiny edge nodes: local dashboards + data push
Extensions you might add:
(planned) interrupt-driven RX with W5500 INT for lower latency
(planned) static IP + watchdog recovery for unattended deployments
Conclusion
To wrap up: the WeAct RP2350A_V20 gives you a modern dual-architecture MCU platform, and WIZnet W5500 gives you a fast path to real Ethernet.
If you want a stable wired IoT node without wrestling with a full TCP/IP stack on the MCU, this is a clean, repeatable approach.
Try it with a W5500 module today, and turn your RP2350A project into a network-ready device.



