Arduino W5500 NTP Client — Get Accurate Time via UDP
Build an Arduino NTP client using the WIZnet W5500 Ethernet Shield to query pool.ntp.org over UDP and display network time.
Monoprice - RJ45 Ethernet Cable
x 1
Introduction
This project implements a classic Network Time Protocol (NTP) client on Arduino using the WIZnet W5500 Ethernet Shield. By sending a 48‑byte UDP request to an NTP server (e.g., pool.ntp.org) and parsing the response, the sketch retrieves the current Unix time, converts it to human‑readable format, and prints it to the Serial Monitor (or an optional LCD).
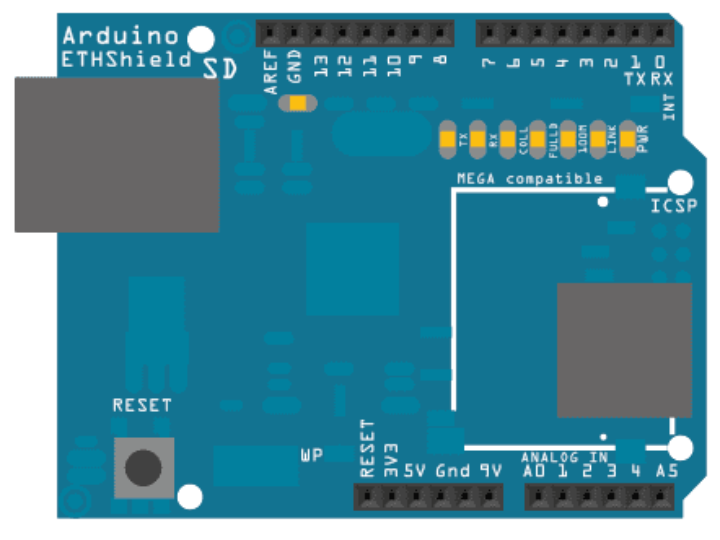
WIZnet Product Integration
The W5500 offloads TCP/IP, providing a reliable wired connection with minimal MCU overhead. The shield interfaces via SPI (ICSP header) and exposes RJ45 with link/activity LEDs. Using EthernetUDP, the sketch opens a UDP socket on port 123, transmits a properly formatted NTP packet, and reads the response.
Technical Implementation
Network Setup
DHCP (recommended): Ethernet.begin(mac); then print Ethernet.localIP().
Static IP (optional): Ethernet.begin(mac, ip); (ensure subnet/gateway match your LAN).
For long‑running DHCP, call Ethernet.maintain() periodically.
NTP Basics
Server: pool.ntp.org (or regional pools).
Port: UDP 123.
Packet: 48 bytes; set LI, VN, Mode bits in the first byte; zero the buffer; send.
Response parsing: Extract the Transmit Timestamp (bytes 40–43) → Unix epoch.
Core Sketch Snippets
1) Init & UDP begin
2) Build & send NTP packet
3) Receive & parse
Core Features and Performance
Reliable wired time sync via NTP over UDP (port 123).
DHCP or static IP options for different network environments.
Simple, lightweight packet handling suitable for 8‑bit MCU.
Applications and Use Cases
Time‑stamping data logs (SD/EEPROM/serial).
Scheduling tasks (alarms, timed relays) without RTC hardware.
Classroom demos on UDP and internet time.
Troubleshooting
No response: try another pool region, check router firewall for UDP/123.
DHCP issues: test with static IP; ensure cable/switch link; consider Ethernet.maintain().
Multiple UDP tasks: use separate EthernetUDP instances or manage ports carefully.
Conclusion
With the WIZnet W5500 Ethernet Shield, Arduino can act as a compact, dependable NTP client. The UDP approach is lightweight and fast, making it ideal for wired IoT nodes that need accurate time without an external RTC.

