Linux_driver-W5500-ethernet
Linux_driver-W5500-ethernet


Linux Driver — W5500 Ethernet
Project Overview
This project aims to deliver a Linux kernel driver for the WIZnet W5500 Ethernet module, making it usable as a standard Ethernet interface (e.g., eth0, eth1) under Linux systems. By integrating SPI communication, device tree configuration, reset control, and interrupt handling, the driver enables embedded Linux boards (including Raspberry Pi, ARM/SoC-based platforms) to communicate over Ethernet using WIZnet W5500.
This work demonstrates WIZnet’s capability in supporting industrial-grade network solutions under Linux, and provides a foundation for R&D in driver optimization, kernel compatibility across versions, and future Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) readiness.
Key Features
Native Linux driver module (or built-into kernel) for WIZnet W5500 over SPI
Device Tree (DT) support: setting up SPI node, CS, IRQ, RST, and other pin configurations
Hardware reset line support (optional) to ensure reliable startup/reset behavior
Network interface registration so users can use standard tools (ifconfig, ip)
Support for both static IP and DHCP methods
Compatibility considerations for different Linux kernel versions
Configuration parameters like SPI speed, interrupt mode, reset polarity, etc.
Hardware Requirements
WIZnet W5500 Module (SPI + CS + RST + optional IRQ)
Linux board / Raspberry Pi or other compatible SoC supporting SPI and Device Tree overlays
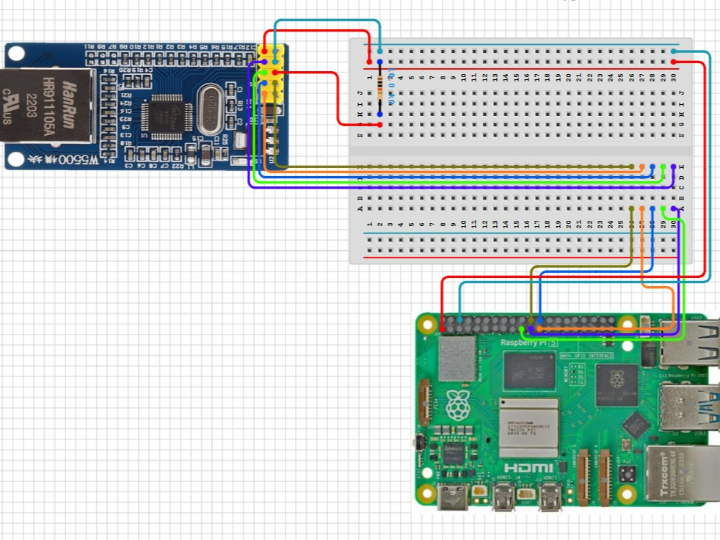
Wiring: correct connections of SPI pins (MOSI, MISO, SCLK, CS), reset pin, optional interrupt pin
Usage / Quick Setup Example
Device Tree Overlay / DTS
Define SPI bus node with correct chip-select, reset GPIO, IRQ if used
Specify spi-max-frequency (e.g-40MHz or suitable speed)
Make sure device tree overlay or board file includes W5500 node
Driver Build / Module Loading
Network Interface Configuration
Testing Connectivity
Technical Challenges & Recommendations
SPI Speed Limitations: Higher SPI clock may cause communication errors if hardware wiring/PCB layout is not optimal
Kernel Version Compatibility: Some APIs / DT syntax change across kernel versions → need back-porting / patching for older kernels
Hardware Reset Support: Ensuring physical reset is supported improves reliability in many embedded applications
Interrupt Handling: For some use-cases, IRQ for link status or event notification may improve performance vs polling
R&D & Strategic Significance
Showcases WIZnet W5500 integration in Linux platform → widens market potential into embedded Linux devices
Provides concrete reference for prospective products that use Linux as OS
Enables internal engineering to consider driver performance improvements, maintainability, and future proofing (SPE, etc.)
Helps in drafting product proposals and techno-commercial documents by having Linux driver as a strong feature
Target Applications
Industrial gateways running Linux (Edge computing devices)
IoT routers / bridge devices that require Ethernet interface via SPI
Custom embedded appliances (e.g., data logging, monitoring) that require wired Ethernet connectivity
OEM / ODM products where Linux is base OS and WIZnet is the Ethernet controller
Contributing & Future Development
Test on multiple Linux kernels (e.g. 5.x, 6.x series) and document compatibility matrix
Enhance driver documentation: overlay examples, wiring schematics, board-specific notes
Add automated testing (link up/down, reset cycles, high throughput)
Potential for integrating Modbus TCP or other higher-layer protocols as modules within Linux
Explore SPE usage, possibly building driver variants optimized for SPE phys or minimized wiring
