How Does NTP Time Synchronization Work on W5500-EVB-PICO?
How Does NTP Time Synchronization Work on W5500-EVB-PICO?
How Does NTP Time Synchronization Work on W5500-EVB-PICO?
An End-to-End Protocol Workflow Using Hardware TCP/IP
(W5500-EVB-PICO에서 NTP 시간 동기화는 어떻게 동작하는가?)
Summary (40–60 words)
This article explains how the W5500-EVB-PICO synchronizes system time using the Network Time Protocol (NTP). By walking through the complete UDP-based NTP workflow—from socket setup to timestamp calculation—it demonstrates how W5500 hardware TCP/IP offloading enables reliable and deterministic time synchronization on embedded Ethernet devices.
1. Why Time Synchronization Matters in Embedded Systems
Accurate system time is essential for many embedded applications, including:
Data logging and traceability
Event ordering and diagnostics
Secure communication and certificates
Distributed control systems
Without time synchronization, logs become unreliable and system behavior is harder to analyze.
NTP provides a lightweight and widely adopted solution for synchronizing time over IP networks.
2. What Is W5500-EVB-PICO?
The W5500-EVB-PICO integrates:
RP2040 MCU (dual-core Cortex-M0+)
WIZnet W5500 Ethernet controller
SPI-based MCU ↔ Ethernet interface
Key architectural principle:
RP2040 handles application logic, while W5500 handles all TCP/UDP/IP protocol processing in hardware.
This separation makes protocol workflows like NTP easier to reason about.
3. NTP Protocol Overview (Embedded Perspective)
NTP is a UDP-based protocol that exchanges timestamps between a client and a server.
Key properties:
Uses UDP port 123
Stateless request–response model
Small packet size (48 bytes)
Designed for low overhead and fast response
For embedded systems, this makes NTP ideal:
No connection management
Minimal memory usage
Deterministic execution path
4. System Architecture for NTP Synchronization
End-to-End Architecture
Important note:
No software UDP/IP stack runs on RP2040
W5500 fully handles UDP packet transmission and reception
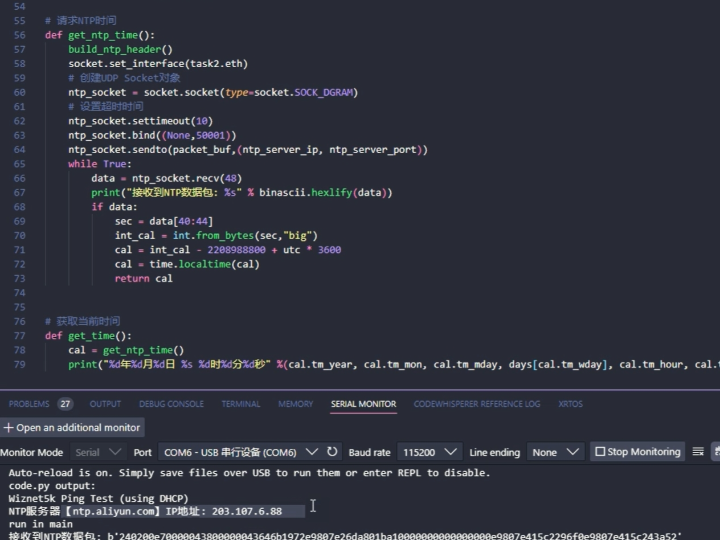
5. End-to-End NTP Workflow on W5500
Step 1: Network Initialization
Configure W5500 common registers
MAC address
IP address (static or DHCP)
Gateway and subnet
Verify link status
Without proper network configuration, NTP cannot proceed.
Step 2: UDP Socket Setup
Select a hardware socket (0–7)
Configure socket mode to UDP
Set local port (arbitrary)
At this point, the socket is ready to send and receive UDP packets.
Step 3: NTP Request Transmission
The W5500 sends the packet immediately over Ethernet.
Step 4: NTP Response Reception
This completes the UDP transaction.
6. Timestamp Calculation and Time Update
The NTP response includes multiple timestamps:
Transmit timestamp (server time)
Receive timestamp
The RP2040 firmware:
Extracts the server timestamp
Converts NTP epoch (1900) to Unix epoch (1970)
Applies timezone or offset if required
Updates the local system clock
This logic is purely application-level and independent of networking.
7. Why Hardware UDP Matters for NTP
With W5500 handling UDP:
Packet checksums are validated in hardware
RX buffering is deterministic
No timing jitter from software stacks
This ensures:
NTP latency and jitter are dominated by network conditions, not firmware behavior.
8. Latency and Accuracy Characteristics
In typical LAN environments:
Round-trip latency is low (milliseconds)
Time accuracy is sufficient for logging and coordination
Single-shot or periodic sync is possible
For most embedded applications:
Sub-second accuracy is more than adequate
9. Common Failure Modes and Debugging Tips
❌ No NTP response received
Cause:
Wrong server IP
UDP port blocked
RX buffer not read
❌ Time updates sporadically
Cause:
RX pointer not advanced
RECV command omitted
❌ Incorrect time value
Cause:
Epoch conversion error
Endianness mismatch
Most issues are application logic errors, not W5500 issues.
10. Why W5500-EVB-PICO Is a Good NTP Reference Platform
Clean hardware TCP/IP offloading
Simple SPI interface
Easy observation of UDP behavior
Deterministic execution
This makes it ideal for:
Time-synced IoT nodes
Gateways and controllers
Networked logging systems
11. Key Takeaway
On W5500-EVB-PICO, NTP synchronization is a straightforward UDP workflow controlled by registers and buffers—not a complex networking problem.
By relying on W5500 hardware:
Firmware stays simple
Time sync remains reliable
Debugging is transparent
FAQ (Engineer-Focused)
Q1. Does W5500 implement NTP internally?
No. W5500 handles UDP; NTP logic runs on the MCU.
Q2. Is TCP required for NTP?
No. NTP uses UDP exclusively.
Q3. How often should time be synchronized?
Depends on clock drift; typically minutes to hours.
Q4. Is this accurate enough for industrial use?
Yes, for logging and coordination tasks.
Q5. Why not use SNTP over Wi-Fi?
Ethernet offers more deterministic timing.
Source
Bilibili video: BV1n1421f7Eg
WIZnet W5500 Datasheet
NTP Protocol Specification (RFC 5905)
Tags
W5500, WIZnet, NTP, Time Synchronization, W5500-EVB-PICO, UDP Protocol, Embedded Ethernet, Industrial IoT
🇰🇷 한국어 번역 (1:1 Full Translation)
W5500-EVB-PICO에서 NTP 시간 동기화는 어떻게 동작하는가?
하드웨어 TCP/IP 기반 NTP 프로토콜 전체 흐름 분석
요약
본 문서는 WIZnet W5500 이더넷 컨트롤러가 탑재된 W5500-EVB-PICO에서 NTP(Network Time Protocol)를 이용해 시스템 시간을 동기화하는 과정을 설명한다. UDP 기반 NTP 프로토콜의 전체 흐름을 분석함으로써, 하드웨어 TCP/IP 오프로딩이 임베디드 시스템에서 안정적인 시간 동기화를 어떻게 가능하게 하는지 보여준다.
1. 임베디드 시스템에서 시간 동기화의 중요성
정확한 시간은
로그, 진단, 시스템 연동의 기본이다.
2. 시스템 아키텍처
3. NTP 동작 흐름
UDP 요청 → 응답 → 타임스탬프 계산
4. 성능 특성
지연과 정확도는
네트워크에 의해 결정된다.
5. 디버깅 포인트
RX 버퍼 처리
포인터 갱신
Epoch 변환
6. 핵심 메시지
W5500 기반 NTP 동기화는 네트워크가 아닌 레지스터 기반 데이터 흐름 문제다.
태그
W5500, WIZnet, NTP, 시간 동기화, 임베디드 이더넷, UDP
