Hardwired TCP/IP Chapter 21: W55MH32 PHY Configuration Example
Hardwired TCP/IP Chapter 21: W55MH32 PHY Configuration Example
Hardwired TCP/IP Chapter 21: W55MH32 PHY Configuration Example
In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation on how to set different PHY modes on the W55MH32 chip. Through practical examples, we will also explain how to configure the PHY mode through software, and flexibly switch the corresponding mode according to different transmission scenarios to reduce power consumption.
Other network protocols used in this example, such as DHCP, please refer to the relevant sections. Regarding the initialization process of W55MH32, please refer to the Network Install section. We will not elaborate on this here.
1 Introduction to the PHY Working Mode
The PHY working mode of the TOE engine of W55MH32 supports two configuration methods. One is configured through the PMODE pin (hardware configuration), and the other is configured through the 5:3 bits of the PHYCFGR register (software configuration). The PHY working mode can be set to 10Mbps (full duplex/s duplex), 100Mbps (full duplex/sduplex), full-function auto negotiation, and power-off mode. The default mode is full-function auto negotiation mode.
Software Configuration Diagram
Note: The configuration through the PMODE pin is only effective upon the initial power-on. Once it is configured via software, it will change to the mode set by the software.
2 The characteristics of different PHY modes
- Rate
- 10BT: The transmission rate is 10 Mbps.
- 100BT: The transmission rate is 100 Mbps.
- 10BT: The transmission rate is 10 Mbps.
- Working mode
- Full-duplex: Allows data to be transmitted simultaneously in both directions, improving network efficiency and bandwidth utilization.
- Half-duplex: At the same time, data can only be transmitted in one direction and cannot be transmitted bidirectionally simultaneously.
- Full-duplex: Allows data to be transmitted simultaneously in both directions, improving network efficiency and bandwidth utilization.
- Power-off mode: The TOE engine stops working. To restore to the normal working state, the TOE engine must be reset.
- Full function, automatic negotiation: Corresponding rates and working modes will be set according to the settings of the opposite interface.
3 Power consumption of different PHY modes
The table below shows the power consumption comparison under different PYH modes:
Status | Minimum | Standard | The greatest | Organization |
100M Link | - | 128 | - | mA |
10M Link | - | 75 | - | mA |
Un-Link (Auto-negotiation mode) | - | 65 | - | mA |
100M Transmitting | - | 132 | - | mA |
10M Transmitting | - | 79 | - | mA |
Power Down mode | - | 13 | - | mA |
4 Application scenario
When we aim to reduce the power consumption of the TOE engine, we can flexibly switch the corresponding rate according to different transmission scenarios, thereby achieving the reduction in power consumption. For example, in the scenario of high-speed transmission, it can be set to the 100Mbps full-duplex mode; while when the TOE engine is not in use, it can be set to the power-off mode, thus effectively saving power consumption.
5 The implementation process
Next, let's take a look at how to set the PHY working mode in the code.
Note: The test instance requires that the PC and W55MH32 be on the same network segment.
Step 1: Set to 100Mbps full-duplex mode
1. /* config init massage */Step 2: Set to 10Mbps half-duplex mode
1. /* setting phy 10M and half-duplex mode */Step 3: Set to power-off mode
1. /* setting phy low power mode */6 Run results
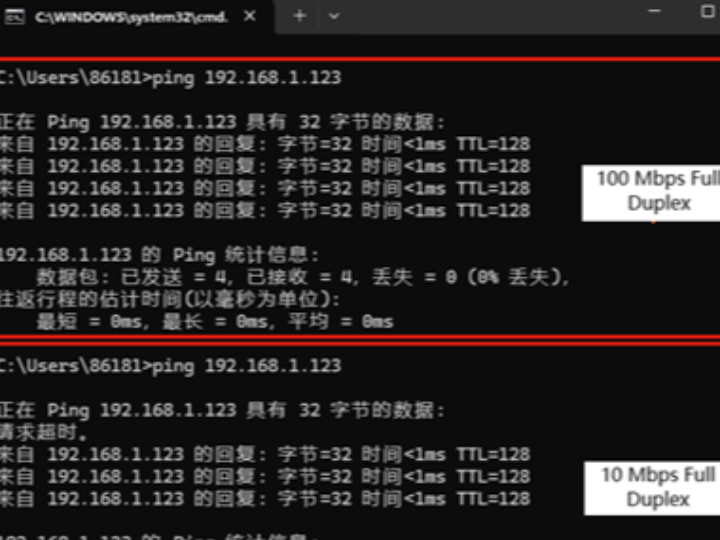
After the burning routine is executed, the first thing you will notice is that the PHY link detection has been performed. Then, the configured network address information is printed. The PHY is set to 100Mbps full-duplex mode, then to 10Mbps half-duplex mode, and finally to the power-off mode. The information is printed as shown in the following figure:
In the power-off mode, it is impossible to ping.
7 Summary
This article explains how to set different PHY modes on the W55MH32 chip. Through practical examples, it demonstrates the process of switching PHY modes between 100Mbps full-duplex, 10Mbps half-duplex, and power-off modes to reduce power consumption based on different transmission scenarios. The article details the configuration methods of PHY working modes, the characteristics of different modes, power consumption differences, and application scenarios, helping readers understand how to optimize the network performance and power consumption of the device in practical applications.
The next article will explain how to implement the MQTT protocol on the W55MH32 and connect to the Alibaba Cloud platform, and achieve data interaction with the Alibaba Cloud object model. Stay tuned!
WIZnet is a non-fabrication semiconductor company founded in 1998. Its products include the Internet processor iMCU™, which adopts TOE (TCP/IP Offloading Engine) technology and is based on a unique patented fully hardwired TCP/IP. iMCU™ is designed for embedded Internet devices in various applications.
WIZnet has over 70 distributors worldwide, with offices in Hong Kong, South Korea, and the United States, providing technical support and product marketing.
The region managed by the Hong Kong office includes: Australia, India, Turkey, and Asia (excluding South Korea and Japan).
