Hardwired TCP/IP Chapter 13: W55MH32 UPnP Port Forwarding Example
Hardwired TCP/IP Chapter 13: W55MH32 UPnP Port Forwarding Example
Hardwired TCP/IP Chapter 13: W55MH32 UPnP Port Forwarding Example
In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation on how to implement the UPnP protocol on the W55MH32 chip. By using the TOE engine of W55MH32, we only need to perform simple socket programming and register reading and writing, and we can easily implement Ethernet applications. Next, through practical examples, we will explain to you how to use the TOE engine to implement the port forwarding function of the UPnP protocol.
Other network protocols used in this example, such as DHCP, please refer to the relevant chapters. Regarding the initialization process of W55MH32, please refer to the Network Install chapter. We will not elaborate on this here.
1 Introduction to the UPnP Protocol
The UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) protocol is a network protocol that enables devices in a local area network to achieve automatic discovery and communication. Its port forwarding function is provided by the IGD Profile, allowing local network devices to dynamically request the router to open specified ports for them, so as to enable external devices to access internal services. This feature eliminates the complexity of manual port forwarding configuration, and is particularly suitable for scenarios that require penetrating the NAT (Network Address Translation) environment.
IGD (Internet Gateway Device) is a part of the UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) protocol. It is mainly used to manage the services and resources of gateway devices (such as routers) in the network. The IGD extension defines a set of standard interfaces, allowing local network devices to communicate with gateway devices, and dynamically configuring network settings, such as port forwarding, bandwidth management, and connection status queries, etc.
2 Characteristics of the UPnP Protocol
- Automated configuration: No need for manual settings by users, reducing the risk of configuration errors.
- Dynamic and flexible: Port mapping rules can be added or deleted dynamically according to requirements.
- Device-friendly: Supports plug-and-play, simplifying the process of device networking and deployment.
- Cross-device compatibility: UPnP is based on standardized protocols and widely supports various devices and platforms.
3 UPnP application scenarios
Through the UPnP port forwarding function, we can utilize the W55MH32 to achieve the following functions:
- Remote access: External requests can be forwarded to local network devices (such as NAS, surveillance cameras), enabling remote access to internal devices from outside.
- Remote control: External devices can be remotely controlled by the UPnP converted ports, allowing for remote control of local network internal devices (smart door locks, lighting controllers).
4 The workflow of setting up port forwarding with UPnP
1. Device discovery: W55MH32 sends multicast requests (HTTP M-SEARCH messages) via SSDP (Simple Service Discovery Protocol) to the local network to search for gateway devices that support IGD.
2. Obtain service description: W55MH32 accesses the gateway device (router) to obtain the service description file to understand the supported services and interfaces.
3. Subscribe to IGD events: Through event subscription, W55MH32 can receive real-time notifications without actively polling.
4. Call service interface: Using UPnP's SOAT messages, W55MH32 calls the port mapping interface provided by IGD.
5. Data interaction test: Externally, communication is conducted by accessing the mapped port and the router address with devices within the local network.
5 Message Explanation
Equipment search
As we mentioned earlier, the SSDP protocol is used during device search. SSDP (Simple Service Discovery Protocol) is a key protocol within the UPnP protocol and is used for device discovery and service publication. It broadcasts and receives messages in the form of HTTP over UDP within the local network, using the multicast address 239.255.255.250 and port 1900.
The SSDP messages are mainly divided into the following categories:
- NOTIFY message (device-initiated broadcast notification): Used by the device to inform the network of its presence or offline status.
- M-SEARCH message (client-initiated search): The client sends a search request to discover the device or service.
- HTTP/1.1 response message (device's response to M-SEARCH): The device's response to the search request, providing the location of the device description file and service information.
SSDP messages are based on the HTTP protocol and have a fixed format, mainly including the following fields:
- HOST: Target address and port, fixed as 239.255.255.250:1900.
- MAN: Used for identifying the search message, fixed as "ssdp:discover" (only used in M-SEARCH).
- MX: Maximum response time, specifies the time within which the device responds (unit: seconds).
- ST: Search target, identifies the type of device or service to be found.
- NT: Notification type, indicates the type of device or service (used in NOTIFY message).
- USN: Unique service name, the unique identifier of the device or service.
- LOCATION: URL of the device description file, containing detailed information of the device.
- CACHE-CONTROL: The caching time of the device information, indicating the validity period of the information.
M-SEARCH request message example:
M-SEARCH * HTTP/1.1Field parsing:HTTP/1.1 200 OKHTTP/1.1 200 OK: This indicates a successful response.Obtaining the device identifier
This step will request an XML file through the HTTP GET method. Regarding the HTTP GET message and HTTP response message, there is no need to elaborate further here. Those interested can refer to the HTTP Client chapter.
Request example:
GET /igd.xml HTTP/1.1Response example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKSubscribe to IGD events
Subscribe to IGD events via HTTP SUBSCRIBE. Example:
SUBSCRIBE /ipc HTTP/1.1Response example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKAdd mapping port message
For example, if we want to map the internal port 8000 of the TCP protocol to the external port 1000, we can make an HTTP request as follows:
POST /ipc HTTP/1.1The descriptions of the main fields are as follows:Response Content:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKDelete port mapping message
For example, if we want to delete the 1000 port that was previously mapped, we can make an HTTP request as follows:
POST /ipc HTTP/1.1The descriptions of the main fields are as follows:
m: DeletePortMapping: Delete Port Mapping
NewExternalPort: External Port Number
NewProtocol: Protocol Type
NewRemoteHost: External Access Source, can be empty
6 The implementation process
In this routine, we have implemented the functions of controlling the LED light switch via serial port, obtaining and setting network address information, conducting TCP and UDP loopback data tests, and adding and deleting mapping ports using UPnP.
Note: The test instance requires the W55MH32 to be connected to a router that supports UPnP port forwarding.
Step 1: Set the size of the Ethernet buffer
1. static uint8_t tx_size[_WIZCHIP_SOCK_NUM_] = {4, 4, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2};
1. /* socket rx and tx buff init */Here, we set the receive and transmit buffers for sockets 0 to 7 to 4KB, 4KB, 2KB, 1KB, 1KB, 1KB, 1KB, and 2KB respectively.
Socket 0 is used for UPnP protocol processing, socket 1 is used for TCP and UDP loopback processing, and socket 2 is used for listening for IGD events.
Step 2: Registration of LED Control Function
1. UserLED_Control_Init(set_user_led_status);The set_user_led_status() function is a function for controlling the LED. The detailed content is as follows:
1. void set_user_led_status(uint8_t val)Step 3: Search for UPnP devices
1. do 1. /**< SSDP Header */In this function, the main operation is to search for IGD devices using the SSDP protocol, and to send messages in a manner consistent with what we have previously described.
Step 4: Obtain the description of the IGD device
1. if (GetDescriptionProcess(SOCKET_ID) == 0) // GET IGD description
1. * @brief This function gets the description message from IGD(Internet Gateway Device).The request message is packaged through the MakeGETHeader() function. The specific message is as follows:
1. /**Then, the received content is parsed through the `parseDescription()` function. If the device description does not support the WANIPConnection service, it indicates that port mapping is not supported, and an error is returned.
The content of the `parseDescription()` function is as follows:
1. /**Step 5: Subscribe to IGD events
1. if (SetEventing(SOCKET_ID) == 0) // Subscribes IGD event messagesThe content of the SetEventing() function is as follows:
1. /**The request message is packaged through the MakeSubscribe() function. The specific message is as follows:
1. /**Finally, the HTTP response message is parsed through the parseHTTP() function to determine whether the subscription was successful.
The parseHTTP() function is as follows:
1. /*-----String Parse Functions-----*/Step 6: Execute the UPnP main program
1. Main_Menu(SOCKET_ID, SOCKET_ID + 1, SOCKET_ID + 2, ethernet_buf, tcps_port, udps_port); // Main menu
1. /**Here, a user option menu will be executed. Options 1 and 2 control the LED switch, options 3 and 4 print and set the network address information, option 5 runs a TCP loopback test program (the loopback test program can be referred to in the TCP Server section), option 6 runs a UDP loopback test program (the loopback test program can be referred to in the UDP section). Option 7 adds an UPnP port mapping table, and option 8 deletes an UPnP port mapping table. Here, we mainly explain options 7 and 8 related to UPnP.
Step 7: Add an UPnP Port Mapping Table
The code is as follows:
1. if (choice[0] == '7')Here, we need the protocol type of the external input port mapping (TCP or UDP), as well as the external port number and the internal port number. After the input is completed, the port number in option 5 or option 6 will be replaced by the input internal port number, and then the port mapping addition processing will be executed through the AddPortProcess() function. The content of the AddPortProcess() function is as follows:
1. /** 1. /**< SOAP header & tail */
1. /**Then, the HTTP header content is created through the MakePOSTHeader() function. The specific content is as follows:
1. /**Finally, the request is sent, and then the response content is parsed using the parseAddPort() function to determine whether the port mapping was successfully added.
1. /**Step 8: Delete an UPnP port mapping table
1. if (choice[0] == '8')Here, we need to specify the protocol type (TCP or UDP) for the external input deletion port mapping, as well as the external port number. After the input is completed, the AddPortMapping processing is executed through the DeletePortProcess() function. The content of the DeletePortProcess() function is as follows:
1. /**First, the XML part of the request message will be assembled through the MakeSOAPDeleteControl() function. The details are as follows:
1. /**Then, the HTTP header content is created through the MakePOSTHeader() function. The specific content is as follows:
1. /**Finally, the request is sent, and then the response content is parsed using the parseDeletePort() function to determine whether the port mapping was successfully added.
1. /**7 Run results
After the burning routine was executed, the PHY link was first detected, and then the network address was obtained through DHCP and the network address information was printed:
Next, search for IGD devices. After the search is successful, the device description will be retrieved and the subscription of IGD events will be set. Once all operations are completed successfully, the main menu will be entered.
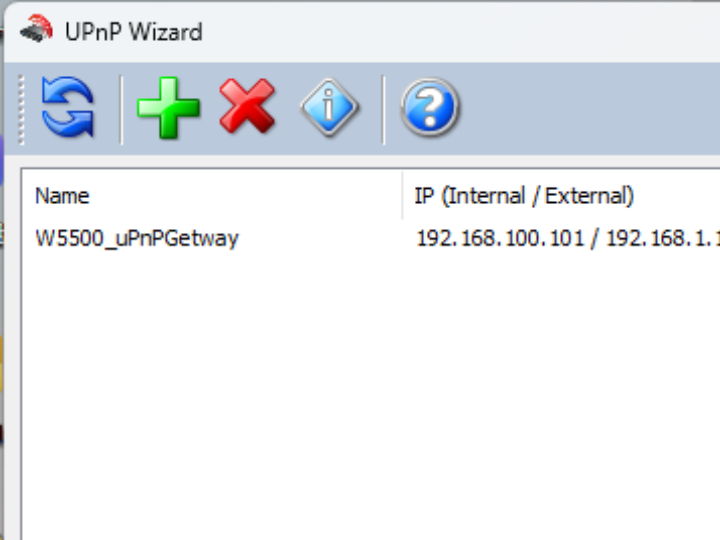
Next, we input 7 and add a TCP protocol port mapping. The external port is 12345 and the internal port is 8000.
we have added. (UPnP Wizard download link: https://upnp-wizard.en.softonic.com/)
Then we input 5 and start the TCP loopback test program.
Subsequently, we opened a network debugging tool, such as SocketTester, and selected the TCP Client mode. The server address was the external IP address, which was 192.168.1.135, and the port number was the external port number 12345. After clicking "Connect" to establish the connection, we could see that it was successfully connected to the internal W55MH32. The same process was followed for UDP, and this will not be demonstrated here.
Then we input "Q" to exit the loop test program, and then input "8" to delete the 12345 external port of the previously added TCP protocol. Click "Refresh" on the UPnP Wizard, and you can see that it has been successfully deleted. Then execute the loop test program again, and you will not be able to connect to the internal W55MH32.
8 Summary
This article explains how to implement the port forwarding function of the UPnP protocol on the W55MH32 chip. Through practical examples, it details the complete process from device search, obtaining device descriptions, subscribing to events, to adding and deleting port mappings, including the protocol messages involved in each step, function implementations, and specific operations. The article also analyzes the introduction, features, and application scenarios of the UPnP protocol, helping readers understand its practical application value in the interconnection of network devices.
The next article will focus on the TFTP protocol, analyzing its core principles and application in file transfer, and explaining how to implement the TFTP function on the W55MH32. Stay tuned!
WIZnet is a non-fabrication semiconductor company founded in 1998. Its products include the Internet processor iMCU™, which adopts TOE (TCP/IP Offloading Engine) technology and is based on a unique patented fully hardwired TCP/IP. iMCU™ is designed for embedded Internet devices in various applications.
WIZnet has over 70 distributors worldwide, with offices in Hong Kong, South Korea, and the United States, providing technical support and product marketing.
The region managed by the Hong Kong office includes: Australia, India, Turkey, and Asia (excluding South Korea and Japan).
