Chapter 38: W55MH32’s Implementing DES / 3DES Hardware Encryption on WIZnet W55MH32
Chapter 38: W55MH32’s Implementing DES / 3DES Hardware Encryption on WIZnet W55MH32
1. Introduction
The WIZnet W55MH32 is a high-performance microcontroller integrating an ARM Cortex-M3 core operating at up to 216 MHz. It includes a hardware algorithms, including DES and 3DES. By leveraging hardware acceleration, the W55MH32 can perform encryption tasks efficiently, reducing CPU load and enhancing data security for embedded applications.\ This application note introduces DES and 3DES, explains ECB and CBC modes, highlights their differences, describes the operation process on W55MH32, outlines their role in SSL/TLS, and identifies suitable application scenarios.
2. Overview of DES and 3DES
DES (Data Encryption Standard)
DES is a symmetric-key algorithm that encrypts data in 64-bit blocks using a 56-bit effective key (out of a 64-bit key, with 8 bits used for parity). DES was widely used historically but is no longer considered secure because its key length is too short to withstand brute-force attacks with modern computing power.
3DES (Triple DES)
3DES is an enhanced version of DES designed to address its security weaknesses. It encrypts data by applying DES operations three times (encrypt-decrypt-encrypt or encrypt-encrypt-encrypt) using either two or three independent keys. This increases the effective key length to 112 bits (2-key 3DES) or 168 bits (3-key 3DES), significantly improving security.
3. Key Differences Between DES and 3DES
Key Length: DES uses a 56-bit effective key, whereas 3DES uses either 112-bit (2-key) or 168-bit (3-key) keys.
Encryption Process: DES performs a single encryption pass, while 3DES performs three DES operations in sequence, typically encrypt-decrypt-encrypt.
Security Level: DES is vulnerable to brute-force attacks; 3DES provides much higher security but is slower due to triple processing.
Performance: 3DES is about one-third the speed of DES because of its triple-pass structure.
Use Cases: DES is obsolete for new designs and should only be used for compatibility. 3DES is stronger and still used in specific legacy systems, but modern applications should prefer AES or similar algorithms.
4. ECB and CBC Modes
ECB (Electronic Codebook Mode)
ECB mode encrypts each 64-bit block of plaintext independently using the same key. Identical plaintext blocks will produce identical ciphertext blocks, which can reveal patterns in the data.
Characteristics:
Simple implementation.
Allows parallel encryption/decryption.
Vulnerable to data pattern leakage, not recommended for sensitive data.
Structure:
Plaintext Block 1 → Encrypt → Ciphertext Block 1
Plaintext Block 2 → Encrypt → Ciphertext Block 2
CBC (Cipher Block Chaining Mode)
CBC mode improves security by XORing each plaintext block with the previous ciphertext block before encryption. The first block is XORed with an initialization vector (IV).
Characteristics:
Prevents pattern leakage (same plaintext block → different ciphertext if positions differ).
Requires a unique IV for each session.
Encryption is sequential (no parallelism), though decryption can be parallelized.
Structure:
Plaintext Block 1 ⊕ IV → Encrypt → Ciphertext Block 1
Plaintext Block 2 ⊕ Ciphertext Block 1 → Encrypt → Ciphertext Block 2
5. Operation Process on W55MH32
The typical operation flow for DES / 3DES on W55MH32 hardware engine involves:
Initialization\ Set up the crypto engine configuration: select DES or 3DES, ECB or CBC mode, input the key(s), and provide the IV if using CBC mode.
Data Processing\ Feed data into the engine in 64-bit (8-byte) blocks. The hardware processes data according to the chosen mode and updates internal state as needed.
Output Handling Retrieve the encrypted or decrypted output from the engine. CBC mode will handle XOR chaining internally; ECB mode processes each block independently.
The hardware engine supports DMA for efficient data transfer during encryption and decryption.
6. Role of DES / 3DES in SSL/TLS
In early SSL and TLS versions (SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1), 3DES in CBC mode was a common choice for securing the confidentiality of data in transit. DES was generally avoided due to its inadequate security.
3DES with CBC was used to encrypt records, often combined with HMAC (e.g., HMAC-SHA1) for integrity checking.
ECB was not used in SSL/TLS due to its vulnerability to pattern leakage.
In modern TLS versions (TLS 1.2 and later), DES and 3DES have been deprecated in favor of stronger algorithms like AES-GCM and ChaCha20-Poly1305.
7. Example Application Scenarios
The W55MH32 DES / 3DES hardware acceleration can be applied in:
POS terminals and financial devices\ Encrypting transaction data between terminals (e.g., POS, ATM) and backend systems to protect against data theft.
Configuration files or firmware protection\ Encrypting firmware binaries or configuration files to prevent unauthorized access or tampering during distribution or storage.
Industrial legacy system compatibility\ Providing encryption support in systems that need to communicate securely with older equipment that uses DES / 3DES.
Database or log file encryption\ Protecting sensitive data stored locally in files or databases, ensuring confidentiality even if storage media is compromised.
8. Progress
For using this hardware DES, it is required to do the following steps.
Step 1: Header files
For activating the DES feature, it is required to include the DES header file from WIZnet's encryption library.
Step 2: DES procedures
In DES procedure, it required to input all variables into the structure for DES and operate DES. It will be the same for EBC and CBC methods but it is required to add an extra IV variables for CBC method.
// Pass all variables into the CallDes structure
// pu8In -- Input data
callDes.pu8In = au8Plain;
// u32InLen indicates the size of input data, in 64-byte units
callDes.u32InLen = DES_TEST_LEN;
// au8Result -- Output data
callDes.pu8Out = au8Result;
// u32OutLen indicates the size of output data, in 64-byte units
callDes.u32OutLen = DES_TEST_LEN;
// u16Opt indicates the method of encrypting messages using ECB
callDes.u16Opt = WIZ_DES_OPT_BLK_ECB | WIZ_DES_OPT_MODE_ENCRYPT;
// pu8Key represents the key for encrypting or decrypting messages
callDes.pu8Key = au8Key;
// Run hardware DES
WIZDES_EncDec(&callDes);For other conditions:
// pu8IV is the IV used for encrypting or decrypting messages
callDes.pu8IV = au8Iv;
// u16Opt is the method selection for decrypting messages using CBC
callDes.u16Opt = WIZ_DES_OPT_BLK_CBC | WIZ_DES_OPT_MODE_DECRYPT;
// u16Opt is the method selection for encrypting messages using 3DES in CBC mode
callTdes.u16Opt = WIZ_DES_OPT_BLK_ECB | WIZ_DES_OPT_MODE_ENCRYPT | WIZ_TDES_OPT_KEY_3;Step 3: Main Code
In this main code, it contains the method for operating DES and 3DES
Main code for DES
void DES_Func_Test()
{
uint8_t i;
uint8_t aucPlain[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x0F, 0x10,
0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14, 0x15, 0x16, 0x17, 0x18, 0x19, 0x1A, 0x1B, 0x1C, 0x1D, 0x1E, 0x1F, 0x20,
0x21, 0x22, 0x23, 0x24, 0x25, 0x26, 0x27, 0x28, 0x29, 0x2A, 0x2B, 0x2C, 0x2D, 0x2E, 0x2F, 0x30,
0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x3A, 0x3B, 0x3C, 0x3D, 0x3E, 0x3F, 0x40};
uint8_t aucDESCipher_ECB[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0x77, 0x81, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x22, 0x67, 0x82, 0x0A, 0x03, 0x7D, 0x05, 0x0F, 0x02, 0xAF, 0xA7,
0x07, 0x01, 0x86, 0x8E, 0x8F, 0x75, 0x65, 0x8B, 0x8D, 0x8E, 0x8F, 0x86, 0x8F, 0x8A, 0x83,
0x00, 0x3B, 0x07, 0x91, 0x0A, 0x56, 0x0A, 0x27, 0x00, 0xFB, 0x12, 0x0F, 0x2E, 0xFE, 0x0A, 0xC2};
uint8_t aucDESCipher_CBC[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0x8B, 0x6D, 0x82, 0x0B, 0x8E, 0x0C, 0x07, 0xF0, 0x06, 0x3F, 0x1F, 0x05, 0x84, 0x0E, 0x0B, 0x91,
0x01, 0x73, 0x0E, 0x81, 0x09, 0x87, 0x03, 0x8D, 0x83, 0x8B, 0x8C, 0x8D, 0x8E, 0x8F, 0x90, 0x91,
0x8B, 0x55, 0x85, 0x59, 0x8B, 0x5F, 0x8B, 0x41, 0x8E, 0xF1, 0x8F, 0x91, 0x8D, 0x65, 0x8C, 0x95,
0x81, 0xF0, 0x8F, 0x2E, 0x0A, 0x56, 0x0F, 0x18, 0x90, 0x0B, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x02, 0x85, 0x01, 0x05};
uint8_t aucResult[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0};
uint8_t aucKey[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
WIZ_SYM_CRYPT_Call callDes;
memset(&callDes, 0, sizeof(callDes));
// ECB ENC
printf("The DES (ECB) data input is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DES_TEST_LEN; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucPlain[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
printf("The DES key is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucKey[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
callDes.pu8In = aucPlain;
callDes.u32InLen = DES_TEST_LEN;
callDes.pu8Out = aucResult;
callDes.pu8IV = NULL;
callDes.u32Op = WIZ_DES_Opt_ECB | WIZ_DES_Opt_MODE_ENCRYPT;
callDes.pu8Key = aucKey;
callDes.u32Crc = WIZCRC_CalcBuff(0xffff, &callDes, sizeof(WIZ_SYM_CRYPT_Call) - 4);
WIZDES_EncDec(&callDes);
// if (0 == memcmp(aucDESCipher_ECB, aucResult, DES_TEST_LEN)), "wiz_des_ecb test\n");
printf("The DES ECB encrypted message is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DES_TEST_LEN; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucResult[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
printf(" \r\n");
printf(" \r\n");
// CBC DEC
printf("The DES (CBC) data input is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DES_TEST_LEN; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucDESCipher_CBC[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
printf("The DES key is \r\n");
}Main code for 3DES
void TDES_Func_Test()
{
uint8_t i;
uint8_t aucPlain[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x0F, 0x10,
0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14, 0x15, 0x16, 0x17, 0x18, 0x19, 0x1A, 0x1B, 0x1C, 0x1D, 0x1E, 0x1F, 0x20,
0x21, 0x22, 0x23, 0x24, 0x25, 0x26, 0x27, 0x28, 0x29, 0x2A, 0x2B, 0x2C, 0x2D, 0x2E, 0x2F, 0x30,
0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x3A, 0x3B, 0x3C, 0x3D, 0x3E, 0x3F, 0x40};
uint8_t aucTDESCipher_ECB[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0x7D, 0x7B, 0x0D, 0x0C, 0xFA, 0x35, 0xB9, 0x49, 0x6A, 0xF8, 0xCE, 0x85, 0xAE, 0x3A, 0x35, 0x00,
0xAC, 0xBD, 0x15, 0x53, 0xE0, 0xC4, 0x3C, 0x90, 0xF9, 0x5C, 0xE5, 0x47, 0xDE, 0xCB, 0x8F, 0x55,
0x6A, 0x3A, 0x15, 0x6D, 0xE8, 0x05, 0x52, 0x8D, 0x16, 0x3A, 0x0E, 0x2B, 0x30, 0x24, 0x37, 0x4E,
0x09, 0x2D, 0x46, 0x06, 0x3C, 0x61, 0x0E, 0xAA, 0x21, 0x5C, 0x0A, 0xFE, 0x3F, 0x42, 0xE8, 0xDD};
uint8_t aucTDESCipher_CBC[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0xAD, 0x17, 0xA7, 0x56, 0x3A, 0x0F, 0xF8, 0xF3, 0x47, 0xB6, 0x3E, 0x78, 0x16, 0x72, 0xCD, 0xD7,
0x6F, 0x52, 0x02, 0x8E, 0xDB, 0x00, 0x49, 0x39, 0x12, 0xD5, 0xB6, 0x8A, 0xD0, 0xCB, 0xDC, 0xC6,
0xFD, 0x98, 0x82, 0x73, 0x18, 0x37, 0xCF, 0x9C, 0x68, 0x10, 0x2E, 0x94, 0x8D, 0x85, 0x2E, 0x09,
0x81, 0x7F, 0x56, 0x70, 0x7E, 0x21, 0xCF, 0x1B, 0x2D, 0x66, 0xD7, 0xE8, 0x96, 0xCC, 0xAC, 0xD4};
uint8_t aucResult[DES_TEST_LEN] = {0};
uint8_t aucKey[24] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x0F, 0x10, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
uint8_t aucIV[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
WIZ_SYM_CRYPT_CALL callTdes;
memset(&callTdes, 0, sizeof(callTdes));
//ECB ENC
printf("The 3DES (ECB) data input is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DES_TEST_LEN; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucPlain[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
printf("The 3DES key is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < 24; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucKey[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
callTdes.pu8In = aucPlain;
callTdes.u32InLen = DES_TEST_LEN;
callTdes.pu8Out = aucResult;
callTdes.u32OutLen = DES_TEST_LEN;
callTdes.u32Op = WIZ_DES_Opt_ECB | WIZ_DES_Opt_MODE_ENCRYPT | WIZ_TDES_Opt_KEY_3;
callTdes.pu8Key = aucKey;
callTdes.u32Crc = WIZCRC_CalcBuff(0xffff, &callTdes, sizeof(WIZ_SYM_CRYPT_CALL) - 4);
WIZTDES_EncDec(&callTdes);
//if (0 == memcmp(aucTDESCipher_ECB, aucResult, DES_TEST_LEN)), "wiz_tdes_ecb test\n");
printf("The 3DES encrypted message is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DES_TEST_LEN; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucResult[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
printf(" \r\n");
printf(" \r\n");
//CBC DEC
printf("The 3DES (CBC) data input is \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DES_TEST_LEN; i++)
{
printf("%02x", aucTDESCipher_CBC[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
}
Step 4: Testing Result
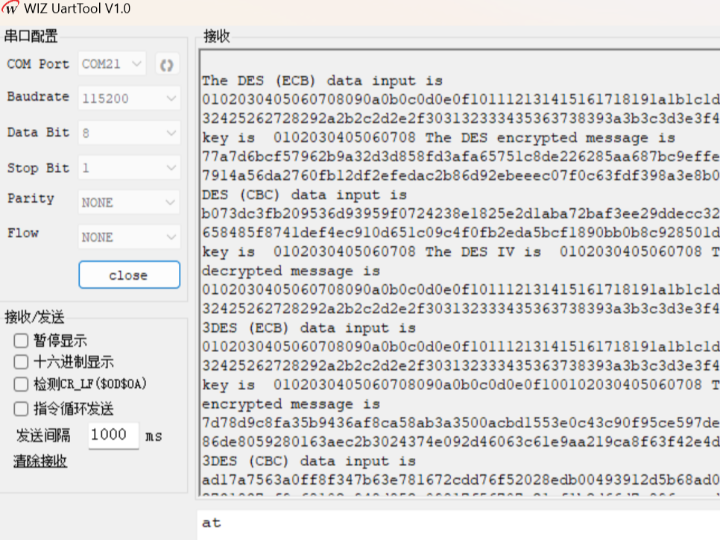
After the program has been downloaded to the W55MH32's EVB, it shows the following results.
DES (All in hex value):
Key and AI value:
0102030405060708Input message (ECB):
0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f101112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f303132333435363738393a3b3c3d3e3f40Encrypted Output message (ECB):
77a7d6bcf57962b9a32d3d858fd3afa65751c8de226285aa687bc9effe26af37003ac7914a56da2760fb12df2efedac2b86d92ebeeec07f0c63fdf398a3e8b04Input message (CBC):
b073dc3fb209536d93959f0724238e1825e2d1aba72baf3ee29ddecc3297bdeb51955658485f8741def4ec910d651c09c4f0fb2eda5bcf1890bb0b8c928501d5Decrypted Output message (CBC):
0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f101112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f303132333435363738393a3b3c3d3e3f403DES (All in hex value):
AI value:
0102030405060708Key value:
0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f100102030405060708Input message (ECB):
0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f101112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f303132333435363738393a3b3c3d3e3f40Encrypted Output message (ECB):
7d78d9c8fa35b9436af8ca58ab3a3500acbd1553e0c43c90f95ce597dec4bf58969a186de8059280163aec2b3024374e092d46063c61e9aa219ca8f63f42e4d2Input message (CBC):
ad17a7563a0ff8f347b63e781672cdd76f52028edb00493912d5b68ad0cbdcc6fd9882731837cf9c68102e948d852e09817f56707e21cf1b2d66d7e896ccacd4Decrypted Output message (CBC):
0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f101112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f303132333435363738393a3b3c3d3e3f40Python results
from des import DesKey
keyDES = DesKey(bytes.fromhex("0102030405060708")) # for DES
key3DES = DesKey(bytes.fromhex("0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f100102030405060708")) # for 3DES, same as "a key for TRIPLEa key fo"
ivDES = bytes.fromhex("0102030405060708") # iv for DES and 3DES
input_text = bytes.fromhex("0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f101112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f303132333435363738393a3b3c3d3e3f40")
des_cbc = bytes.fromhex("b073dc3fb209536d93959f0724238e1825e2d1aba72baf3ee29ddecc3297bdeb51955658485f8741def4ec910d651c09c4f0fb2eda5bcf1890bb0b8c928501d5")
tdes_cbc = bytes.fromhex("ad17a7563a0ff8f347b63e781672cdd76f52028edb00493912d5b68ad0cbdcc6fd9882731837cf9c68102e948d852e09817f56707e21cf1b2d66d7e896ccacd4")
# DES ECB Encrypt
print("DES ECB Encryption:")
print(bytes.hex(keyDES.encrypt(input_text)))
# DES CBC Decrypt
print("DES CBC Decryption:")
print(bytes.hex(keyDES.decrypt(des_cbc, initial=ivDES)))
# 3DES ECB Encrypt
print("3DES ECB Encryption:")
print(bytes.hex(key3DES.encrypt(input_text)))
# 3DES CBC Decrypt
print("3DES CBC Decryption:")
print(bytes.hex(key3DES.decrypt(tdes_cbc, initial=ivDES)))8. Conclusion
The DES / 3DES hardware engine of the WIZnet W55MH32 provides embedded systems with an efficient and low-power symmetric encryption solution, significantly reducing CPU workload while enhancing data security and integrity. By supporting both ECB and CBC modes, W55MH32 meets diverse encryption requirements --- with ECB suited for simple use cases and CBC for applications demanding stronger protection against data pattern leakage. While DES is considered obsolete due to its short key length, 3DES still plays a role in financial and industrial applications that require compatibility with legacy systems. For new designs, modern algorithms such as AES are recommended to achieve stronger security. The hardware encryption capabilities of W55MH32 offer embedded developers a flexible and reliable foundation for secure communications, firmware protection, and local data storage.
