IoT Based Smart Energy Meter Using Modbus Protocol as Electricity Saving Effort
This paper introduces a smart energy meter system that leverages IoT technology and the Modbus protocol to remotely monitor and manage electrical energy consump
As electricity consumption becomes an integral part of daily life, accurately measuring and managing usage is crucial for both consumers and utility providers. This study presents a smart energy meter system designed to optimize energy consumption by utilizing the Internet of Things (IoT) and Modbus protocol.
Key Components and Findings:
Smart Energy Meter:
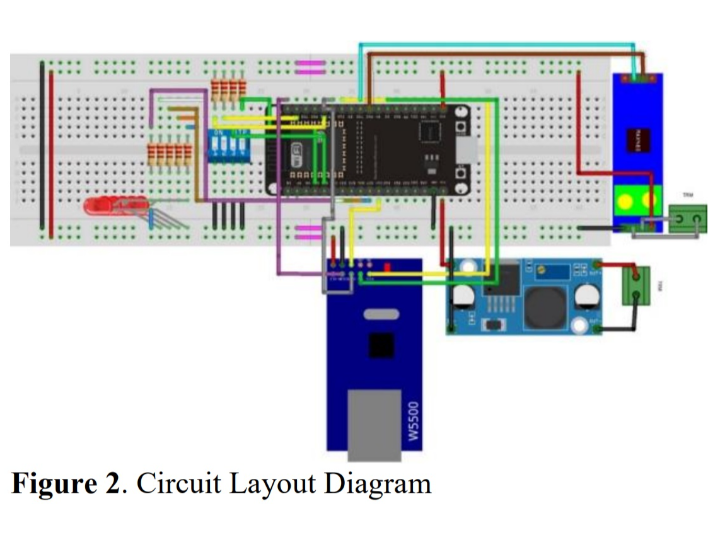
- Hardware Design: The system uses a digital power meter, microcontroller ESP32, RS-485 to TTL converter, Ethernet module W5500, current transformer (CT), and additional electronic components such as dip switches and LEDs. The microcontroller acts as the central controller, interfacing with the power meter and communicating data to the cloud.
- WIZnet W5500 Ethernet Module: Facilitates internet connectivity for real-time data transmission to cloud servers, enabling remote monitoring and control of energy usage.
Communication Protocols:
- Modbus Protocol: Employed for communication between the microcontroller and power meter, allowing reliable data exchange over the RS-485 network.
- MQTT Protocol: Used for sending power meter data to the cloud, supporting real-time updates on energy consumption accessible via computers or smartphones.
System Architecture:
- The control system comprises several components, including a digital power meter, ESP32 microcontroller, and Ethernet module. The power meter data is read through the Modbus protocol and transmitted to a cloud-based platform using MQTT. Users can access this data remotely to monitor their energy usage.
- Power Meter Data: Collected data includes current, voltage, power, and energy consumption. This information is analyzed and displayed on user interfaces to provide insights into electricity usage patterns.
Benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: The system enables consumers to track and manage their electricity usage, promoting efficient consumption and reducing wastage.
- Cost Savings: By providing real-time data, users can identify excessive usage and take corrective actions, potentially lowering electricity bills.
- Remote Accessibility: Offers the convenience of monitoring energy consumption remotely, enhancing user experience and accessibility.
Experimental Results:
- The study tested the smart energy meter system's performance, demonstrating accurate data transmission and real-time monitoring capabilities. The system successfully provided users with actionable insights into their energy usage, highlighting areas for improvement and efficiency.
Implementation Challenges:
- Technical Complexity: Developing and integrating the system requires expertise in IoT and networking technologies.
- Data Security: Ensuring the secure transmission of data over the internet is a critical consideration in system design.
Hashtags: #SmartEnergy #IoT #Modbus #WIZnet #W5500 #EnergyEfficiency #RemoteMonitoring #ElectricitySaving Categories: Internet of Things (IoT), Energy Management, Smart Metering, Electrical Engineering, Automation
Publish Date: 2022

