How Does W5500 Behave on RT-Thread with STM32L496?
This article analyzes a real RT-Thread implementation using STM32L496 and the WIZnet W5500 Ethernet controller.
How Does W5500 Behave on RT-Thread with STM32L496?
SPI Frame Format, CS Timing, and Throughput Behavior in an RTOS Environment
(STM32L496 + RT-Thread 환경에서 W5500은 어떻게 동작하는가?)
Summary (40–60 words)
This article analyzes a real RT-Thread implementation using STM32L496 and the WIZnet W5500 Ethernet controller. By focusing on SPI frame format, chip-select timing, and throughput behavior under an RTOS, it explains how correct low-level driver design enables stable TCP communication and predictable performance in multitasking embedded systems.
1. Why RTOS + Ethernet Is a Different Problem
Using Ethernet on a bare-metal MCU is already non-trivial.
Using Ethernet inside an RTOS introduces additional challenges:
Task preemption during SPI transfers
Concurrent access to the Ethernet driver
Timing-sensitive chip-select (CS) handling
Performance degradation due to context switching
This makes RT-Thread + STM32L496 + W5500 a valuable real-world case study.
Most Ethernet bugs in RTOS systems are not protocol bugs—they are SPI timing bugs.
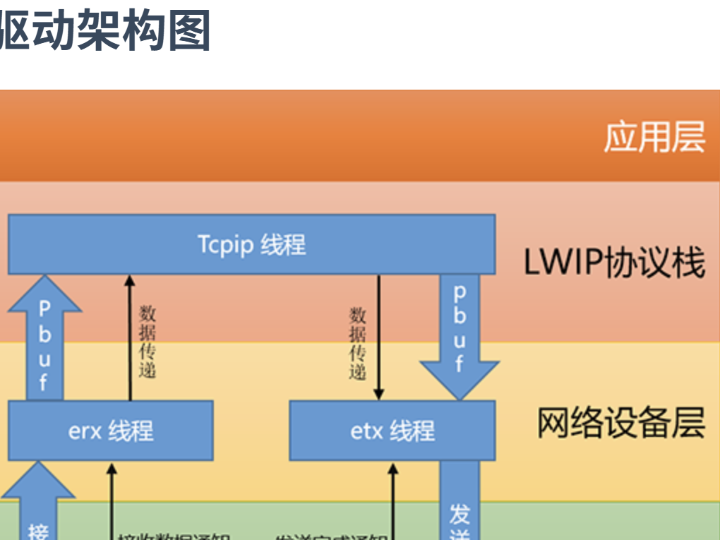
2. System Architecture Overview
RT-Thread Ethernet Stack with W5500
Key architectural decision:
TCP/IP is implemented inside W5500 hardware
RT-Thread does not run a software TCP/IP stack for W5500
RTOS tasks interact only with driver APIs
3. W5500 SPI Frame Format (Why CS Timing Matters)
Every W5500 SPI transaction follows a strict frame structure:
16-bit address (block + offset)
8-bit control field
Block select
Read / Write
Data length mode (VDM / FDM)
Data bytes
Critical Rule
CS must remain asserted for the entire SPI frame.
If CS toggles mid-frame:
Address decoding breaks
Register writes become undefined
TX/RX pointers corrupt silently
This is especially dangerous in RTOS environments.
4. CS Timing Behavior Under RT-Thread
The Core RTOS Problem
In RT-Thread:
SPI transfers can be preempted
Multiple threads may request SPI access
DMA or interrupt-based SPI complicates timing
If CS is not protected:
Task switch may occur mid-transfer
CS deasserts too early
W5500 interprets an incomplete frame
Correct RTOS-Safe Design
Wrap SPI + CS control inside a critical section
Use mutex/semaphore around W5500 driver
Ensure one logical W5500 operation = one SPI transaction
This rule is non-negotiable.
5. Register and Buffer Access in an RTOS Context
W5500 exposes:
Common registers
Socket registers
TX/RX buffers
In RT-Thread, the driver must ensure:
No two tasks access TX/RX buffers concurrently
Pointer updates are atomic
SEND / RECV commands are serialized
Failure here leads to:
send() returns OK but no data sent
RX size non-zero but recv fails
TCP stalls without obvious error
6. Throughput Behavior on STM32L496 + W5500
What Determines Throughput?
In this architecture, throughput is influenced by:
SPI clock frequency
SPI transaction efficiency
Task scheduling latency
TX/RX buffer size allocation
Not by TCP/IP complexity (handled by hardware).
Observed Practical Behavior
Small packets suffer from RTOS overhead
Larger contiguous transfers approach SPI bandwidth limits
Poor CS handling dramatically reduces throughput
Throughput problems often indicate driver inefficiency, not network issues.
7. RTOS-Specific Performance Pitfalls
❌ Pitfall 1: Per-byte SPI Transfers
Excessive CS toggling
Massive overhead
Low throughput
❌ Pitfall 2: Unprotected SPI Access
Race conditions
Random TCP failures
❌ Pitfall 3: Frequent Context Switching
Increased latency
Reduced effective bandwidth
✔ Recommended Approach
Batch buffer reads/writes
Use block transfers
Minimize task switches during SPI operations
8. Debugging Strategy for RT-Thread + W5500
Experienced engineers debug in this order:
Logic analyzer on SPI + CS
Verify full-frame CS assertion
Check TX/RX pointer consistency
Monitor socket state transitions
Measure throughput vs SPI clock
Never start by debugging TCP.
9. Why W5500 Works Well with RTOS
Despite RTOS complexity, W5500 remains robust because:
TCP state machines are hardware-driven
Retransmissions are deterministic
RTOS jitter does not affect TCP correctness
As long as SPI discipline is respected, the system is stable.
10. Key Takeaway
In RT-Thread systems, W5500 reliability and performance depend almost entirely on correct SPI frame and CS timing—not on TCP logic.
When the driver is designed correctly:
TCP becomes predictable
Throughput scales with SPI efficiency
RTOS multitasking does not break networking
FAQ (Engineer-Focused)
Q1. Does RT-Thread run TCP/IP for W5500?
No. W5500 handles TCP/IP entirely in hardware.
Q2. Why is CS timing more critical under RTOS?
Because tasks can preempt SPI transfers.
Q3. Is DMA safe to use with W5500 SPI?
Yes, but CS must remain asserted until DMA completes.
Q4. What limits throughput most?
SPI efficiency and task scheduling, not TCP.
Q5. Is this applicable to FreeRTOS as well?
Yes. The principles are RTOS-agnostic.
Source
CNBlogs article (whylinux)
WIZnet W5500 Datasheet
RT-Thread documentation
Tags
W5500, STM32L496, RT-Thread, SPI CS Timing, Embedded Ethernet, TCP Performance, RTOS Ethernet Driver, Industrial Networking
🇰🇷 한국어 번역 (1:1 Full Translation)
RT-Thread + STM32L496 환경에서 W5500은 어떻게 동작하는가?
SPI 프레임 구조, CS 타이밍, 처리량 관점 분석
요약
본 문서는 RT-Thread 환경에서 STM32L496과 WIZnet W5500을 연동한 실제 사례를 분석한다. SPI 프레임 구조와 CS 타이밍, 그리고 RTOS 환경에서의 처리량 특성을 중심으로, 올바른 저수준 드라이버 설계가 TCP 통신 안정성과 성능을 어떻게 보장하는지를 설명한다.
1. RTOS에서 이더넷이 어려운 이유
RTOS는 멀티태스킹을 제공하지만
SPI 타이밍에는 새로운 위험 요소를 만든다.
2. 시스템 아키텍처
3. SPI 프레임과 CS 타이밍
CS는 프레임 전체 동안 유지되어야 한다.
4. RTOS 환경의 CS 문제
태스크 전환은
SPI 프레임을 망가뜨릴 수 있다.
5. 처리량 분석
성능은 TCP가 아니라
SPI 효율로 결정된다.
6. 디버깅 핵심
SPI + CS 파형 확인
포인터 일관성
태스크 보호
7. 핵심 메시지
RT-Thread에서 W5500의 성능과 안정성은 SPI 드라이버 품질에 달려 있다.
태그
W5500, STM32L496, RT-Thread, SPI 타이밍, RTOS 이더넷, 처리량 분석
