ESP32 & W5500-Based Asynchronous MQTT Temperature & Humidity Monitoring System
This project uses ESP32 with a W5500 to collect temperature and humidity data from a DHT22 sensor and send it to an MQTT broker using async communication.
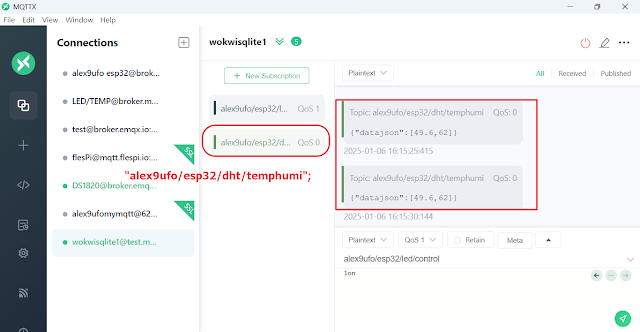
1. Project Overview & Features
Core Functionality:
- This project reads temperature and humidity data from a DHT22 sensor and transmits it to an MQTT broker via W5500 Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- The system supports asynchronous MQTT communication using the AsyncMQTT_ESP32 library, ensuring efficient and non-blocking message handling.
Problem Solved & Use Case:
- Allows real-time remote monitoring of environmental conditions.
- Ideal for IoT applications, such as smart home automation and industrial monitoring.
Key Features:
- Hardware: ESP32, W5500 Ethernet module, DHT22 sensor
- Network: Supports both Ethernet (W5500) and Wi-Fi connectivity
- Protocol: MQTT
- Data Handling: JSON-based message formatting for structured transmission
2. Hardware & Software Stack
Hardware Components:
- Microcontroller: ESP32
- Network Module: W5500 Ethernet (SPI Interface)
- Sensor: DHT22 Temperature & Humidity Sensor
Software Components:
- Programming Language: C++ (Arduino IDE)
- Libraries Used:
- AsyncMQTT_ESP32: Non-blocking MQTT communication
- Adafruit Sensor & DHT_U: Sensor data collection
- ArduinoJson: JSON data formatting
- Network Protocols: MQTT, TCP/IP
3. Key Parts of the Source Code
Ethernet Connection Setup
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize Ethernet
Ethernet.init(ETH_CS_PIN);
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
// Setup MQTT broker connection
mqttClient.setServer(MQTT_HOST, MQTT_PORT);
mqttClient.setCallback(mqttCallback);
}void connectToMqtt() {
while (!mqttClient.connected()) {
Serial.print("Connecting to MQTT...");
if (mqttClient.connect("ESP32Client")) {
Serial.println("Connected");
// Subscribe to a topic
mqttClient.subscribe("sensor/data");
} else {
Serial.print("Failed, rc=");
Serial.print(mqttClient.state());
Serial.println(" Retrying in 5 seconds...");
delay(5000);
}
}
}void readSensorData() {
sensors_event_t event;
dht.temperature().getEvent(&event);
float temperature = event.temperature;
dht.humidity().getEvent(&event);
float humidity = event.relative_humidity;
// Format data as JSON
StaticJsonDocument<256> doc;
doc["temperature"] = temperature;
doc["humidity"] = humidity;
char jsonBuffer[512];
serializeJson(doc, jsonBuffer);
// Publish data to MQTT topic
mqttClient.publish("sensor/data", jsonBuffer);
}3. Comparison with Traditional MQTT Implementations
✅ Advantages:
Asynchronous Processing:
- Uses AsyncMQTT_ESP32 for non-blocking communication.
- Improves system responsiveness and efficiency.
Better Scalability:
- Compatible with various boards, including ESP32 and multiple Ethernet modules (W5500, ENC28J60, etc.).
❌ Disadvantages:
Increased Complexity:
- Asynchronous programming requires a deeper understanding compared to traditional synchronous implementations.
Library Dependency:
- The project heavily relies on AsyncMQTT_ESP32, which may require maintenance and updates to remain compatible.
4. Suggested Improvements & Enhancements
✔ Security: Implement TLS/SSL encryption for MQTT to enhance data security.
✔ Error Handling: Add mechanisms to detect and handle network failures, sensor errors, and MQTT disconnections.
✔ Data Storage: Enable local storage (SD card) or cloud-based database integration for long-term data logging.
✔ Real-time Monitoring: Integrate with Node-RED or other visualization tools to display real-time sensor data.


