The W5100Sio-M module uses network timed tasks via the SNTP protocol.
The W5100Sio-M module uses network timed tasks via the SNTP protocol.
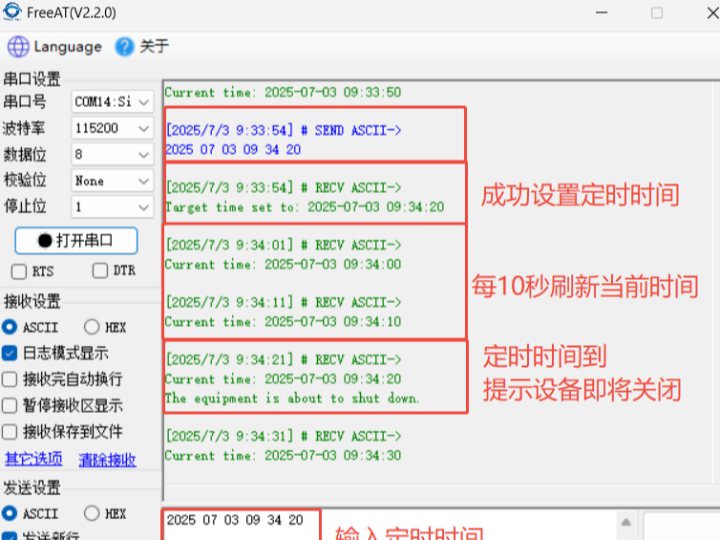
Table of contents
1. Introduction
2. Project Environment
2.1 Hardware Environment
2.2 Software Environment
3 Hardware Connection and Solution
3.1 W5100S Hardware Connection
3.2 Scheme Diagram
4. Introduction to Timestamps and Time Zones
4.1 Introduction to Timestamps
4.2 Introduction to Time Zones
5. Routine Modification
5.1 Modification of main.c file
5.2 wiz_platform file
6. Timed Testing
7. Summary
1. Introduction
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) is a network time protocol based on UDP, primarily used for synchronizing the time of devices in a computer network. SNTP aims to provide a simple time calibration service. Compared to NTP (Network Time Protocol), SNTP is simpler in function and has relatively lower accuracy , typically with errors ranging from tens to hundreds of milliseconds .
The W5100Sio-M is a high-performance SPI-to-Ethernet module launched by Weishi, with the following features:
Minimalist design: integrates MAC, PHY, 16KB cache and RJ45 network port, directly connects to the main controller via 4-wire SPI interface, 3.3V power supply, compact size suitable for embedded scenarios.
Simple and easy to use: Users no longer need to port the complex TCP/IP protocol stack to the MCU, and can directly develop based on application layer data.
Abundant resources: Provides a wealth of MCU application examples and hardware reference designs that can be directly referenced and used, greatly shortening the development time. Hardware is compatible with the W5500io-M module, facilitating solution development and iteration.
Wide range of applications: It is widely used in industrial control, smart grid, charging piles, security and fire protection, new energy, energy storage and other fields.
Product Link: Product Details
2. Project Environment
2.1 Hardware Environment
W5100Sio-M
STM32F103VCT6 EVB
Network cable
DuPont wires
Switch or router
2.2 Software Environment
Example program link : https://www.w5100S.com
FeisiChuang Serial Port Assistant
S NTP server address
Keil5
3 Hardware Connection and Solution
3.1 W5100S Hardware Connection
1. //W5100S_SCS ---> STM32_GPIOD7 /*W5100S的片选引脚*/
2. //W5100S_SCLK ---> STM32_GPIOB13 /*W5100S的时钟引脚*/
3. //W5100S_MISO ---> STM32_GPIOB14 /*W5100S的MISO引脚*/
4. //W5100S_MOSI ---> STM32_GPIOB15 /*W5100S的MOSI引脚*/
5. //W5100S_RESET---> STM32_GPIOD8 /*W5100S的RESET引脚*/
6. //W5100S_INT ---> STM32_GPIOD9 /*W5100S的INT引脚*/
3.2 Scheme Diagram
4. Introduction to Timestamps and Time Zones
4.1 Introduction to Timestamps
SNTP uses a single request-response model for time synchronization: the client sends a request to the time server, and the server returns the current timestamp. A timestamp is a unique and sequential digital code generated based on a specific starting point (such as January 1, 1970). It is used to accurately mark and prove the specific point in time when an event occurred. Its core function is to provide immutable proof of time and determine the order in which events occurred. It is widely used in areas such as system logs, data security (such as digital signatures and blockchain), and file records.
4.2 Introduction to Time Zones
After obtaining Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) via SNTP, you need to perform addition and subtraction operations based on your time zone to calculate your local time. For example, China is located in the UTC+8 time zone, defined as 39 in the example code. Therefore, you need to add 8 hours after obtaining UTC to convert it to Chinese time.
00)UTC-12:00 Baker Island, Howland Island (both uninhabited)
01) UTC-11:00 American Samoa, Samoa
02) UTC-10:00 (Summer)French Polynesia (most), United States (Aleutian Islands, Hawaii)
03) UTC-09:30 Marquesas Islands
04) UTC-09:00 Gambier Islands;(Summer)United States (most of Alaska)
05) UTC-08:00 (Summer)Canada (most of British Columbia), Mexico (Baja California)
06) UTC-08:00 United States (California, most of Nevada, most of Oregon, Washington (state))
07) UTC-07:00 Mexico (Sonora), United States (Arizona); (Summer)Canada (Alberta)
08) UTC-07:00 Mexico (Chihuahua), United States (Colorado)
09) UTC-06:00 Costa Rica, El Salvador, Ecuador (Galapagos Islands), Guatemala, Honduras
10) UTC-06:00 Mexico (most), Nicaragua;(Summer)Canada (Manitoba, Saskatchewan), United States (Illinois, most of Texas)
11) UTC-05:00 Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador (continental), Haiti, Jamaica, Panama, Peru
12) UTC-05:00 (Summer)Canada (most of Ontario, most of Quebec)
13) UTC-05:00 United States (most of Florida, Georgia, Massachusetts, most of Michigan, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Washington D.C.)
14) UTC-04:30 Venezuela
15) UTC-04:00 Bolivia, Brazil (Amazonas), Chile (continental), Dominican Republic, Canada (Nova Scotia), Paraguay,
16) UTC-04:00 Puerto Rico, Trinidad and Tobago
17) UTC-03:30 Canada (Newfoundland)
18) UTC-03:00 Argentina; (Summer) Brazil (Brasilia, Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo), most of Greenland, Uruguay
19) UTC-02:00 Brazil (Fernando de Noronha), South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
20) UTC-01:00 Portugal (Azores), Cape Verde
21) UTC±00:00 Cote d'Ivoire, Faroe Islands, Ghana, Iceland, Senegal; (Summer) Ireland, Portugal (continental and Madeira)
22) UTC±00:00 Spain (Canary Islands), Morocco, United Kingdom
23) UTC+01:00 Angola, Cameroon, Nigeria, Tunisia; (Summer)Albania, Algeria, Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina,
24) UTC+01:00 Spain (continental), Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Kinshasa, Kosovo,
25) UTC+01:00 Macedonia, France (metropolitan), the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland
26) UTC+02:00 Libya, Egypt, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe, (Summer)Bulgaria, Cyprus, Estonia,
27) UTC+02:00 Finland, Greece, Israel, Jordan, Latvia, Lebanon, Lithuania, Moldova, Palestine, Romania, Syria, Turkey, Ukraine
28) UTC+03:00 Belarus, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Iraq, Kenya, Madagascar, Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast), Saudi Arabia,
29) UTC+03:00 South Sudan, Sudan, Somalia, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Yemen
30) UTC+03:30 (Summer)Iran
31) UTC+04:00 Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Mauritius, Oman, Russia (European), Seychelles, United Arab Emirates
32) UTC+04:30 Afghanistan
33) UTC+05:00 Kazakhstan (West), Maldives, Pakistan, Uzbekistan
34) UTC+05:30 India, Sri Lanka
35) UTC+05:45 Nepal
36) UTC+06:00 Kazakhstan (most), Bangladesh, Russia (Ural: Sverdlovsk Oblast, Chelyabinsk Oblast)
37) UTC+06:30 Cocos Islands, Myanmar
38) UTC+07:00 Jakarta, Russia (Novosibirsk Oblast), Thailand, Vietnam
39) UTC+08:00 China, Hong Kong, Russia (Krasnoyarsk Krai), Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, most of Mongolia, Western Australia
40) UTC+09:00 Korea, East Timor, Russia (Irkutsk Oblast), Japan
41) UTC+09:30 Australia (Northern Territory);(Summer)Australia (South Australia))
42) UTC+10:00 Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai); (Summer)Australia (New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria)
43) UTC+10:30 Lord Howe Island
44) UTC+11:00 New Caledonia, Russia (Primorsky Krai), Solomon Islands
45) UTC+11:30 Norfolk Island
46) UTC+12:00 Fiji, Russia (Kamchatka Krai);(Summer)New Zealand
47) UTC+12:45 (Summer)New Zealand
48) UTC+13:00 Tonga
49) UTC+14:00 Kiribati (Line Islands)5. Routine Modification
5.1 Modification of main.c file
The W51 00Sio-M module connects to an SNTP server via network to obtain accurate time, sets the timezone to China (UTC+8, represented by the value 39 in line 25 of the code), and sets the target time via serial port. When the system time reaches or exceeds the target time, a shutdown prompt message is output. Furthermore, a refresh mechanism is included, updating and displaying the current time every 10 seconds.
Lines 171-200 check if the set time is greater than the current time.
Lines 132-170 check if the date is a valid date ( considering leap years ).
Lines 235-278 set the date format and range for the timer (the date format for the timer is: YYYY MM DD HH MM SS).
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "wiz_platform.h"
#include "wizchip_conf.h"
#include "wiz_interface.h"
#include "do_dns.h"
#include "sntp.h"
#define SOCKET_ID 0
#define ETHERNET_BUF_MAX_SIZE (1024 * 2)
#define UART_BUF_SIZE 64
// 网络配置
wiz_NetInfo default_net_info = {
.mac = {0x00, 0x08, 0xdc, 0x12, 0x22, 0x12},
.ip = {192, 168, 1, 30},
.gw = {192, 168, 1, 1},
.sn = {255, 255, 255, 0},
.dns = {8, 8, 8, 8},
.dhcp = NETINFO_DHCP};
uint8_t ethernet_buf[ETHERNET_BUF_MAX_SIZE] = {0};
uint8_t sntp_server_name[] = "cn.pool.ntp.org";
uint8_t sntp_server_ip[4] = {0};
uint8_t timezone = 39; // china
datetime date = {0};
// 目标时间相关变量
datetime target_time = {0};
uint8_t target_set = 0;
uint8_t triggered = 0;
// 串口输入缓冲区
uint8_t uart_buf[UART_BUF_SIZE];
uint8_t uart_index = 0;
// 时间打印控制变量
uint8_t first_print = 1; // 首次打印标志
uint32_t last_print_time = 0; // 上次打印时间
void process_uart_command(void);
void print_current_time(void);
uint8_t is_valid_date(datetime *dt);
uint8_t is_later_than_current(datetime *target);
int main(void)
{
delay_init();
debug_usart_init();
wiz_timer_init();
wiz_spi_init();
wiz_rst_int_init();
printf("%s SNTP example\r\n", _WIZCHIP_ID_);
/* wizchip init */
wizchip_initialize();
network_init(ethernet_buf, &default_net_info);
if (do_dns(ethernet_buf, sntp_server_name, sntp_server_ip))
{
printf("DNS request failed.\r\n");
while (1);
}
SNTP_init(SOCKET_ID, sntp_server_ip, timezone, ethernet_buf);
printf("System ready. Enter target time (YYYY MM DD HH MM SS):\r\n");
while (1)
{
// 处理串口输入
if (uart_index > 0) {
process_uart_command();
}
// 获取当前时间
if (SNTP_run(&date))
{
// 首次打印
if(first_print) {
print_current_time();
first_print = 0;
last_print_time = date.ss;
}
// 每10秒打印一次
if((date.ss % 10) == 0 && date.ss != last_print_time) {
print_current_time();
last_print_time = date.ss;
}
// 检查是否到达目标时间
if (target_set && !triggered)
{
if (date.yy == target_time.yy &&
date.mo == target_time.mo &&
date.dd == target_time.dd &&
date.hh == target_time.hh &&
date.mm == target_time.mm &&
date.ss >= target_time.ss)
{
printf("The equipment is about to shut down.\r\n");
triggered = 1;
}
// 检查是否已经过了目标时间
else if (date.yy > target_time.yy ||
(date.yy == target_time.yy && date.mo > target_time.mo) ||
(date.yy == target_time.yy && date.mo == target_time.mo && date.dd > target_time.dd) ||
(date.yy == target_time.yy && date.mo == target_time.mo && date.dd == target_time.dd && date.hh > target_time.hh) ||
(date.yy == target_time.yy && date.mo == target_time.mo && date.dd == target_time.dd && date.hh == target_time.hh && date.mm > target_time.mm) ||
(date.yy == target_time.yy && date.mo == target_time.mo && date.dd == target_time.dd && date.hh == target_time.hh && date.mm == target_time.mm && date.ss > target_time.ss))
{
printf("Target time has already passed.\r\n");
target_set = 0;
triggered = 0;
}
}
}
delay_ms(100); // 防止忙等待
}
}
void print_current_time(void)
{
printf("Current time: %04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\r\n",
date.yy, date.mo, date.dd, date.hh, date.mm, date.ss);
}
// 检查日期是否有效
uint8_t is_valid_date(datetime *dt)
{
// 检查月份
if (dt->mo < 1 || dt->mo > 12) {
return 0;
}
// 检查日
if (dt->dd < 1) {
return 0;
}
// 检查各月份的天数
uint8_t days_in_month;
switch (dt->mo) {
case 2:
// 检查闰年:能被4整除但不能被100整除,或者能被400整除
if ((dt->yy % 4 == 0 && dt->yy % 100 != 0) || (dt->yy % 400 == 0)) {
days_in_month = 29;
} else {
days_in_month = 28;
}
break;
case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:
days_in_month = 30;
break;
default:
days_in_month = 31;
break;
}
if (dt->dd > days_in_month) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
// 检查目标时间是否晚于当前时间
uint8_t is_later_than_current(datetime *target)
{
// 先比较年份
if (target->yy > date.yy) return 1;
if (target->yy < date.yy) return 0;
// 同年比较月份
if (target->mo > date.mo) return 1;
if (target->mo < date.mo) return 0;
// 同月比较日
if (target->dd > date.dd) return 1;
if (target->dd < date.dd) return 0;
// 同日比较小时
if (target->hh > date.hh) return 1;
if (target->hh < date.hh) return 0;
// 同小时比较分钟
if (target->mm > date.mm) return 1;
if (target->mm < date.mm) return 0;
// 同分钟比较秒
if (target->ss > date.ss) return 1;
// 目标时间等于或早于当前时间
return 0;
}
void process_uart_command(void)
{
// 确保字符串以null结尾
uart_buf[uart_index] = '\0';
// 移除可能的回车换行符
for(uint8_t i = 0; i < uart_index; i++) {
if(uart_buf[i] == '\r' || uart_buf[i] == '\n') {
uart_buf[i] = '\0';
uart_index = i;
break;
}
}
// 解析命令
int values[6];
int count = sscanf((char*)uart_buf, "%d %d %d %d %d %d",
&values[0], &values[1], &values[2],
&values[3], &values[4], &values[5]);
if (count == 6)
{
// 创建临时时间结构体
datetime temp_time;
temp_time.yy = values[0];
temp_time.mo = values[1];
temp_time.dd = values[2];
temp_time.hh = values[3];
temp_time.mm = values[4];
temp_time.ss = values[5];
// 验证年份范围
if(temp_time.yy < 2000 || temp_time.yy > 2100) {
printf("Error: Year must be between 2000-2100\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 验证月份范围
if(temp_time.mo < 1 || temp_time.mo > 12) {
printf("Error: Month must be between 1-12\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 验证日期有效性(考虑闰年)
if (!is_valid_date(&temp_time)) {
printf("Error: Invalid date (e.g. Feb 29 in non-leap year)\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 验证小时范围
if(temp_time.hh < 0 || temp_time.hh > 23) {
printf("Error: Hour must be between 0-23\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 验证分钟范围
if(temp_time.mm < 0 || temp_time.mm > 59) {
printf("Error: Minute must be between 0-59\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 验证秒钟范围
if(temp_time.ss < 0 || temp_time.ss > 59) {
printf("Error: Second must be between 0-59\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 检查是否已获取当前时间
if (date.yy == 0) {
printf("Error: Current time not available yet. Please wait...\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 检查目标时间是否晚于当前时间
if (!is_later_than_current(&temp_time)) {
printf("Error: Target time must be later than current time\r\n");
uart_index = 0;
return;
}
// 设置目标时间
target_time = temp_time;
target_set = 1;
triggered = 0;
printf("Target time set to: %04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\r\n",
target_time.yy, target_time.mo, target_time.dd,
target_time.hh, target_time.mm, target_time.ss);
}
else
{
printf("Invalid format. Expected 6 numbers separated by spaces.\r\n");
printf("Example: 2025 07 02 17 20 00\r\n");
}
// 重置缓冲区
uart_index = 0;
}5.2 wiz_platform file
To ensure that the time setting command input from the serial port can be reliably received, an interrupt mechanism can be used to handle serial port input: when a character is input from the serial port, the interrupt service routine is immediately triggered to capture each character in real time; even if the main program is busy handling network communication or other tasks, the interrupt can be responded to first to ensure that the input characters are not lost, thereby achieving timely reception of the time setting command.
void debug_usart_init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
/* config USART1 clock */
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_USART1 | RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
/* USART1 GPIO config */
/* Configure USART1 Tx (PA.09) as alternate function push-pull */
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
/* Configure USART1 Rx (PA.10) as input floating */
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_10;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
/* USART1 mode config */
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = 115200;
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Rx | USART_Mode_Tx;
USART_Init(USART1, &USART_InitStructure);
// 使能接收中断
USART_ITConfig(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE, ENABLE);
// 配置USART1中断
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = USART1_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 0;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 0;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
USART_Cmd(USART1, ENABLE);
}
// 修改USART1_IRQHandler函数
void USART1_IRQHandler(void)
{
if (USART_GetITStatus(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE) != RESET)
{
uint8_t ch = USART_ReceiveData(USART1);
// 只处理可打印字符
if(ch >= 32 && ch <= 126) {
// 将字符存入缓冲区
if (uart_index < (UART_BUF_SIZE - 1))
{
uart_buf[uart_index++] = ch;
}
}
// 处理回车或换行符
else if(ch == '\r' || ch == '\n') {
if(uart_index > 0) {
// 触发命令处理
uart_buf[uart_index] = '\0';
// 这里不重置uart_index,让主循环处理
}
}
USART_ClearITPendingBit(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE);
}
}6. Timed Test
7. Summary
This article introduces a network timing control solution based on the SNTP protocol using the W5100Sio-M module. With the appropriate hardware and software, the module connects to an SNTP server to obtain the time, adapting to the UTC+8 time zone. The system supports setting a target time via serial port, refreshing the current time display every 10 seconds, and triggering an alert upon reaching the target time. It provides a reliable timing solution for industrial control and other scenarios, offering simple and practical operation. Thank you for your patience in reading! If you have any questions during the reading process, or would like to learn more about this product and its applications, please feel free to leave a message via private message or in the comments section. We will reply to your message as soon as possible to provide you with more detailed answers and assistance!
