How Does Understanding W5500 Registers and SPI Framing Simplify TCP and UDP Development?
This article explains how understanding the WIZnet W5500 register architecture and SPI frame format enables developers to build TCP and UDP communication easily
How Does Understanding W5500 Registers and SPI Framing Simplify TCP and UDP Development?
(W5500 레지스터와 SPI 구조를 이해하면 TCP·UDP 개발이 왜 쉬워질까?)
Summary (40–60 words)
This article explains how understanding the WIZnet W5500 register architecture and SPI frame format enables developers to build TCP and UDP communication easily and reliably. By mastering block selection, socket registers, and SPI transaction rules, users can avoid common pitfalls and focus on application logic instead of low-level network protocol complexity.
1. Why Many Beginners Struggle with TCP/UDP on Embedded Ethernet
When developers first use Ethernet on microcontrollers, the difficulty rarely comes from TCP or UDP concepts themselves. Instead, most problems originate from:
Misunderstanding how registers are organized
Writing to the wrong memory block
Breaking SPI transactions by toggling CS incorrectly
Confusing socket registers with TX/RX buffers
The WIZnet W5500 is designed to eliminate software TCP/IP complexity, but it still requires correct register and SPI access.
Once this foundation is understood, TCP and UDP development becomes straightforward.
2. W5500 Design Philosophy: Hardware TCP/IP, Software Simplicity
The W5500 integrates the following in hardware:
TCP, UDP, ICMP, ARP, IPv4
Ethernet MAC and PHY
32 KB internal buffer memory
8 independent hardware sockets
This means:
The MCU does not implement a TCP/IP stack
The MCU only configures registers and moves data
TCP/UDP behavior is deterministic and stable
To take advantage of this design, developers must understand how to talk to the chip correctly over SPI.
3. SPI Frame Structure: The Foundation of All Network Operations
Every operation—setting an IP address, opening a socket, sending TCP data—uses the same SPI frame structure.
W5500 SPI Transaction Phases
This structure is fixed and universal.
Why This Matters for TCP/UDP
If the block select bits are wrong → wrong register or buffer
If CS toggles early → transaction is aborted
If mode bits are wrong → data length is misinterpreted
All TCP/UDP bugs caused by SPI usually trace back to these three mistakes.
4. Register Blocks: One Chip, Many Logical Regions
The W5500 memory map is divided into logical blocks, not flat memory.
4.1 Common Register Block (Global Network Identity)
This block defines who the device is on the network.
Key registers include:
MAC address (SHAR)
IP address (SIPR)
Subnet mask (SUBR)
Gateway (GAR)
PHY status (PHYCFGR)
Chip version (VERSIONR)
📌 Why TCP/UDP Depends on This
If these registers are incorrect, no socket will ever work, regardless of TCP or UDP logic.
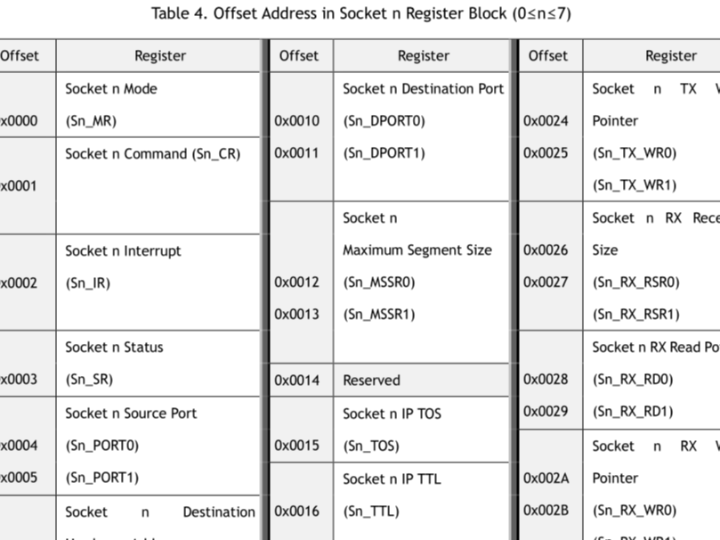
4.2 Socket Register Blocks (8 Identical Sets)
W5500 provides 8 identical socket register blocks, each controlling one communication channel.
Each socket has:
Mode (TCP / UDP)
Source port
Destination IP/port
Status and interrupt flags
📌 Why This Simplifies TCP/UDP
TCP and UDP use the same socket concept
Switching protocol is just a register configuration
No protocol stack rewrite is required
5. TX and RX Buffers: Where TCP/UDP Data Really Lives
The W5500 contains:
16 KB TX memory
16 KB RX memory
Shared across 8 sockets
Each socket gets a configurable portion.
Important Concept
TX/RX buffers are not general RAM
They are accessed through SPI with block selection
For TCP:
TX buffer = data to send
RX buffer = received stream data
For UDP:
TX buffer = datagram payload
RX buffer = packet payload + metadata
📌 Why Understanding This Matters
Once developers know:
Which block to select
How offsets wrap
How CS defines the transaction
TCP and UDP data handling becomes predictable and simple.
6. Variable Length Mode (VDM): Why CS Timing Is Critical
Most applications use VDM (Variable Length Data Mode).
In VDM:
Data length is not predefined
CS LOW duration defines transaction length
This means:
One CS LOW must cover the entire SPI frame
Impact on TCP/UDP
Partial CS toggling = corrupted packet
DMA without proper CS handling = random socket errors
Correct CS handling = stable long-term communication
This explains why SPI discipline is essential for reliable networking.
7. How This Knowledge Directly Enables TCP Development
With correct understanding:
Configure Common Registers (MAC/IP)
Configure Socket n registers (TCP mode)
Write payload to TX buffer
Trigger SEND command
Read RX buffer for response
No TCP retransmission logic.
No state machine implementation.
No protocol parsing.
The W5500 does it in hardware.
8. How This Knowledge Directly Enables UDP Development
UDP development becomes even simpler:
Configure Common Registers
Configure Socket n registers (UDP mode)
Write datagram to TX buffer
Send
Read RX buffer when interrupt occurs
The same SPI rules and register concepts apply.
9. Why This Architecture Is Ideal for Education and Industrial IoT
Education
Clear hardware-software separation
No hidden TCP/IP stack
Easy debugging via registers
Industrial IoT
Deterministic behavior
Low MCU load
Long-term stability
Reduced firmware complexity
This is why W5500 is widely used in industrial Ethernet products.
10. Key Takeaway for New WIZnet Users
Once you understand W5500 registers and SPI framing, TCP and UDP become configuration tasks, not protocol implementations.
This is the core value of WIZnet hardware TCP/IP.
FAQ
Q1. Do I need to understand TCP internals to use W5500?
No. You only need to understand registers and SPI access.
Q2. Why is CS handling so important?
Because SPI transactions define packet boundaries in VDM mode.
Q3. Is UDP easier than TCP on W5500?
Yes, but both use the same socket and buffer model.
Q4. Can beginners really use this chip?
Yes. The learning curve is front-loaded on SPI and registers, not TCP.
Q5. Why is this better than software TCP/IP stacks?
It reduces RAM usage, CPU load, and firmware complexity.
Tags
W5500, WIZnet, SPI Ethernet, Register Architecture, TCP Client, UDP Communication, Hardware TCP/IP, Embedded Networking, Industrial IoT
W5500 레지스터와 SPI 구조를 이해하면 TCP·UDP 개발이 왜 쉬워질까?
요약
본 문서는 WIZnet W5500의 레지스터 구조와 SPI 프레임 방식을 이해함으로써 TCP 및 UDP 통신을 얼마나 쉽게 구현할 수 있는지를 설명한다. 블록 선택, 소켓 레지스터, SPI 트랜잭션 규칙을 정확히 이해하면 네트워크 프로토콜 구현 부담 없이 안정적인 통신이 가능해진다.
1. 임베디드 TCP/UDP에서 초보자가 어려움을 겪는 이유
대부분의 문제는 TCP 자체가 아니라:
레지스터 접근 오류
SPI 프레임 이해 부족
CS 타이밍 문제
버퍼 접근 실수
에서 발생한다.
W5500은 TCP/IP를 하드웨어로 처리하지만, 올바른 접근 방법은 반드시 필요하다.
2. W5500의 설계 철학
W5500은 다음을 하드웨어로 제공한다.
TCP, UDP, ICMP, ARP, IPv4
MAC + PHY
32 KB 내부 버퍼
8개 하드웨어 소켓
MCU는 설정과 데이터 이동만 담당한다.
3. SPI 프레임 구조의 중요성
모든 네트워크 동작은 동일한 SPI 구조를 사용한다.
이 구조를 깨뜨리면 TCP/UDP는 동작하지 않는다.
4. 레지스터 블록 이해
공통 레지스터
MAC, IP, Gateway 설정 담당
→ 네트워크 정체성
소켓 레지스터
TCP/UDP 통신 채널 제어
→ 프로토콜은 설정으로 결정
5. TX/RX 버퍼 구조
TX = 송신 데이터
RX = 수신 데이터
8개 소켓이 메모리를 공유
올바른 블록 선택이 필수다.
6. CS 타이밍과 VDM 모드
VDM에서는 CS가 데이터 길이를 정의한다.
CS를 잘못 제어하면 패킷이 깨진다.
7. TCP 개발이 쉬워지는 이유
TCP는:
소켓 설정
버퍼 쓰기
SEND 명령
만으로 동작한다.
8. UDP 개발이 쉬워지는 이유
UDP 역시 동일한 구조를 사용하며 더 단순하다.
9. 교육 및 산업용 가치
교육: 구조가 명확
산업: 안정성과 결정성 확보
10. 핵심 메시지
W5500에서 TCP·UDP의 핵심은 레지스터와 SPI 이해다.
태그
W5500, WIZnet, SPI 이더넷, 레지스터 구조, TCP, UDP, 임베디드 네트워크, 산업용 IoT
