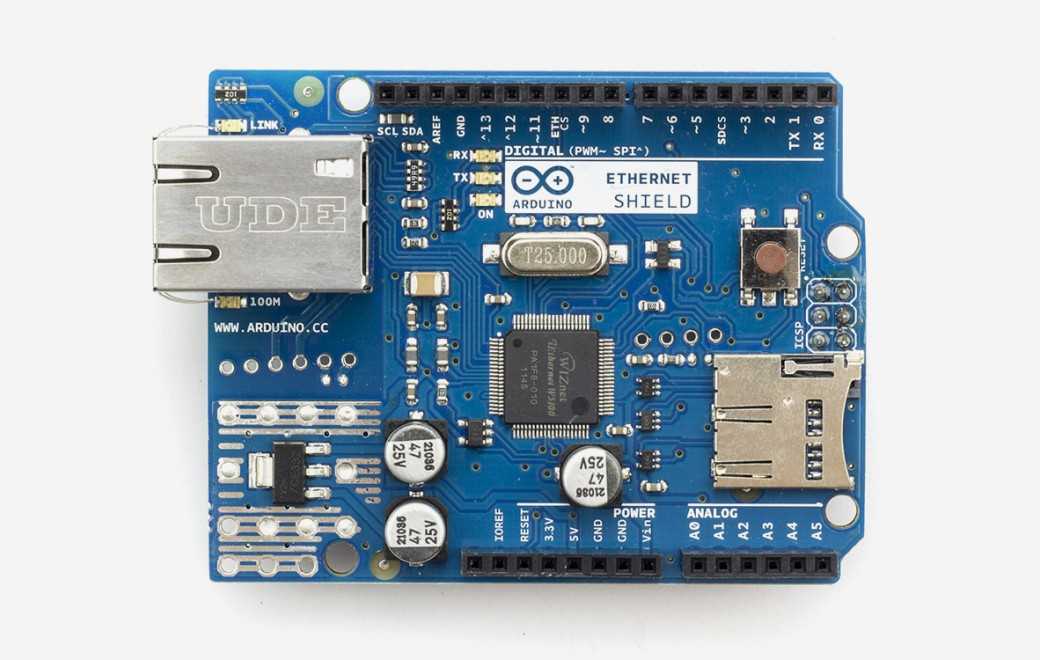
PoliTOcean-EVA–Distributed Underwater Robot Control System Based on Arduino Ethernet Shield
EVA ROV is a distributed control underwater robot system connecting multiple microcontrollers via wired Ethernet and MQTT protocol for real-time communication.
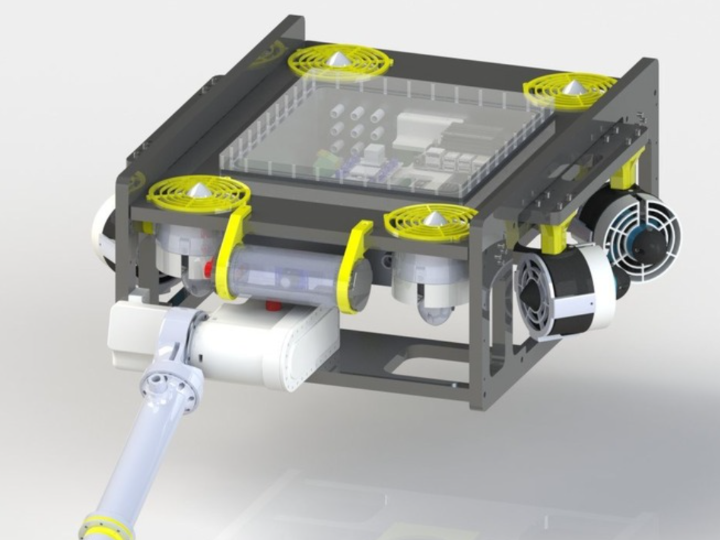
EVA ROV – Distributed Underwater Robot Control System Based on Arduino Ethernet Shield
Project Overview
EVA ROV is a distributed control underwater robot system constructed by connecting multiple microcontrollers via wired Ethernet, developed by PoliTOcean, the prestigious marine robotics team from Politecnico di Torino (Turin Polytechnic University), Italy.
About PoliTOcean Team:
PoliTOcean represents Italy's leading academic excellence in marine robotics, comprising elite engineering students and researchers from one of Europe's top technical universities. The team has established itself as a formidable competitor in international underwater robotics competitions, particularly the MATE ROV (Marine Advanced Technology Education) World Championship, where they consistently demonstrate cutting-edge engineering solutions and innovative system architectures.
Technical Innovation:
Overcoming the limitations of traditional single-MCU ROV architectures, this system implements a groundbreaking structure where each functional module operates independently and communicates in real-time through the MQTT protocol. This distributed approach reflects the team's deep understanding of industrial-grade system design and their commitment to pushing the boundaries of underwater robotics technology.
Real-World Validation:
Validated in actual educational and competition environments including international MATE ROV competitions, this system demonstrates the team's capability to deliver mission-critical solutions. The system seamlessly integrates and controls all subsystems including sensors, robotic arm, lighting, power, and propulsion through a single wired network, showcasing the sophisticated engineering expertise that PoliTOcean brings to marine technology.
Academic Excellence:
As representatives of Politecnico di Torino, ranked among the top engineering institutions globally, the PoliTOcean team embodies the Italian tradition of engineering excellence, combining theoretical rigor with practical innovation. Their work on EVA ROV serves as a benchmark for distributed underwater robotics systems and demonstrates how academic research can directly translate into competition-winning technology.
This project exemplifies how Italy's premier engineering minds are advancing the frontiers of marine robotics through innovative distributed system architectures.
System Architecture
EVA ROV consists of 5 independent MCU nodes communicating via Ethernet-based MQTT.
Surface Control GUI (Python / MQTT)
│
────────────── Ethernet Tether ───────────────
10.0.0.2 10.0.0.4 10.0.0.5 10.0.0.6 10.0.0.3
┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│Sensors │ │Camera │ │Power │ │Robot Arm│ │Propulsion │
│ATMega │ │ATMega │ │ATMega │ │ATMega │ │STM32 │
│Ethernet │ │Ethernet │ │Ethernet│ │Ethernet │ │Ethernet │
└─────────┘ └─────────┘ └────────┘ └─────────┘ └────────────┘
Core Design Principles
- 5 MCU nodes, each independently connected via Ethernet
- Module-to-module message exchange through MQTT Pub/Sub structure
- Stable network based on 10.0.0.x static IP addressing
- Minimized latency through wired Ethernet (essential for underwater environments)
Hardware Configuration
1. Sensor Node (ATMega, 10.0.0.2)
Composed of IMU (LSM9DS1), depth sensor (MS5837), and temperature sensor (BMP280), it publishes sensor data via MQTT at 500ms intervals. Connected to the network through the Ethernet Shield's SPI interface.
2. Camera & Lighting Node (ATMega, 10.0.0.4)
Handles servo motor-based camera tilt control and 2-channel PWM LED lighting. Receives MQTT commands to adjust camera angle and lighting brightness in real-time.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include "Adafruit_MQTT.h"
3. Power Management Node (ATMega, 10.0.0.5)
Monitors voltage, current, and temperature based on LT PMBus and controls 12V line relays. Reports real-time power status to the surface control station via MQTT.
4. Robot Arm Node (ATMega, 10.0.0.6)
Controls robotic arm rotation with stepper motors and drives a PWM-based gripper. Operates by receiving OPEN, CLOSE, and STOP commands via MQTT.
Ethernet.init(53);
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip_arm);
5. Propulsion Node (STM32 Nucleo, 10.0.0.3)
Controls Blue Robotics T200 thrusters and executes attitude calculation and stabilization algorithms. Developed based on PlatformIO and Arduino framework.
Network Communication – MQTT over Ethernet
All nodes connect to the MQTT server (10.0.0.254) through Ethernet Shield.
Common Code Pattern
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
Adafruit_MQTT_Client mqtt(&client, AIO_SERVER, 1883, USERNAME);
mqtt.subscribe(&topic);
Stability Features
- 15ms timeout setting ensures immediate responsiveness
- Auto-reconnection routine guarantees network stability
- Wired connection minimizes packet loss
Surface Control System
Provides the following features through Python and Qt-based GUI:
- Real-time display of IMU, depth, voltage, and other data
- Camera streaming
- Joystick-based remote control
- Data logging in CSV format
- Bidirectional control based on MQTT communication
Vision Processing System
EVA ROV implements OpenCV-based vision processing capabilities for MATE ROV competition mission execution.
- Fish life/death detection algorithm
- Line tracking system
- Shipwreck size measurement and map stitching
- Hough Transform-based object recognition
- Model training in Google Colab environment
Why Ethernet?
Since Wi-Fi cannot be used in underwater environments, wired Ethernet is essentially mandatory. This project satisfies the following requirements based on Ethernet Shield.
- Immediate Responsiveness: Low latency within 15ms
- Precise Real-Time Control: Accurate synchronization of thrusters and robotic arm
- High Reliability: Stable communication without packet loss
- Distributed System Scalability: Architecture that facilitates module addition
Ethernet Shield Implementation
The firmware of this project is written in a structure fully compatible with W5100/W5500 series Ethernet Shields.
Key Points
- Based on Ethernet.h library for compatibility with various Ethernet modules
- Uses Arduino Ethernet Shield in actual system
- Expandable to ENC28J60, ESP32 Ethernet Bridge, etc.
- Simple maintenance with SPI-centric interface
A design that secures stable Ethernet communication required for underwater robots without being dependent on specific chips.
Conclusion
EVA ROV is a practical project that fully applies distributed control architecture based on Arduino Ethernet Shield and MQTT to an underwater robot system.
Key Features
- Field-validated modular design
- Stable wired Ethernet-based communication
- Complete distributed system composed of sensors, robotic arm, power, propulsion, and lighting
- Full-stack robotics construction including Python GUI, OpenCV, and STM32
With a structure suitable for education, competitions, research, and industrial applications, it serves as an excellent reference for Ethernet-based robot networking.