Pluviometro arduino(Arduino-based Pluviometer Project Curation)
Pluviometro arduino(Arduino-based Pluviometer Project Curation)
Arduino-based Pluviometer Project Curation
Project Overview: This project involves creating a pluviometer using Arduino and an Ethernet shield to measure rainfall and display the data in real-time through a web browser or Excel. This system effectively functions as a basic weather station, DIY-style, allowing for more efficient collection and analysis of rainfall data.
Core Components:
- Arduino Uno
- Ethernet Shield
- RTC (Real-Time Clock) Shield
- Standard Tilting-Type Pluviometer
- 10Kohm Resistor
- 0.1uF Capacitor
Operating Principle:
- The pluviometer measures rainfall by tilting as it collects a specific amount of water (0.2mm of rainfall), causing it to tip and empty its contents.
- Arduino detects each tilting action and records the rainfall amount. Each tilt is detected through an interrupt pin on Arduino, logging 0.2mm of rainfall.
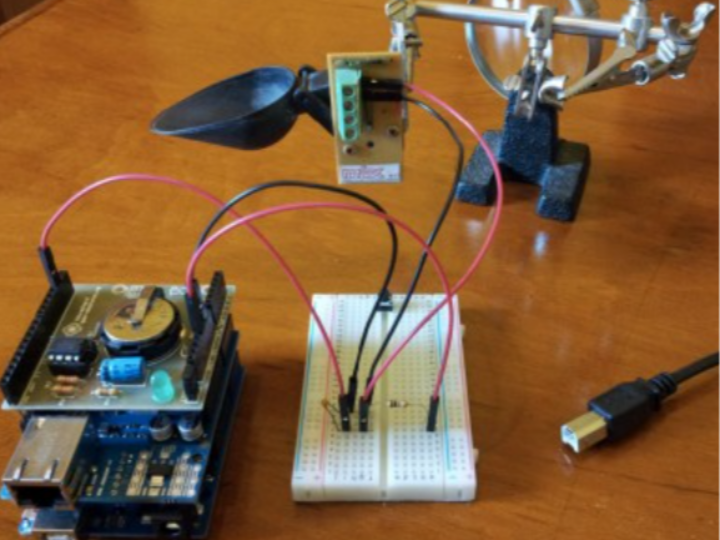
Electrical Circuit Configuration:
- The circuit uses a simple resistor and capacitor to minimize the 'chattering' phenomenon of the tilting switch, ensuring that multiple signals are processed as one for accurate rainfall measurements.
Sketch (Code) Features:
- Connected to the local network via an Ethernet shield, it runs a web server capable of transmitting rainfall data to a web page.
- Saves rainfall data on an SD card in CSV format, which can be directly accessed through Excel.
- Utilizes an RTC to timestamp the data accurately.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "RTClib.h"
#include <Ethernet.h>
RTC_DS1307 RTC;
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
byte ip[] = { 192,168,1, 130 };
EthernetServer server(80); //imposta il server a rispondere sulla porta 80
float TotPioggia;
String strNow;
boolean blnWrite=false;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Start");
Wire.begin(); //inizializzo libreria per protocollo I2C
RTC.begin(); //inizializzo libreria RTC
RTC.sqw(1); //0 Led off - 1 Freq 1Hz - 2 Freq 4096kHz - 3 Freq 8192kHz - 4 Freq 32768kHz
if (! RTC.isrunning()) {
Serial.println("RTC is not running!");
RTC.adjust(DateTime(__DATE__, __TIME__)); //imposta RTC con orario del pc
}
//attivo interrupt 0 dove si passa da 5V a 0V quando il pluvio bascula
attachInterrupt(0, Basculata, FALLING); //LOW CHANGE RISING FALLING
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
server.begin();
Serial.print("Server is at ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
if (!SD.begin(4)) {
Serial.println("Card failed, or not present");
return;
}
Serial.println("Card initialized.");
}
void loop(){
String strTmp;
DateTime now = RTC.now();
strTmp="";
strTmp=strTmp+now.day() + "/";
strTmp=strTmp+now.month() + "/";
strTmp=strTmp+now.year() + " ";
strTmp=strTmp+now.hour() + ":";
strTmp=strTmp+now.minute() + ":";
strTmp=strTmp+now.second();
strNow=strTmp;
Serial.println(strNow);
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client) { //verifico esistenza connessione da parte di un client
boolean currentLineIsBlank = true;
while (client.connected()) { //ciclo fino a che la connessione del client è attiva
if (client.available()) { //verifico sempre che il client comunichi con il server
char c = client.read(); //leggo dal client la richiesta della pagina
if (c == '\n' && currentLineIsBlank) { //se la richiesta è un car di linea nuova inizio comunicazione con il client
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
client.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML>");
client.println("<html>");
client.println("<h2>Arduino: Dati acquisiti di Pluviometria:</h2>");
File htmlFile = SD.open("rain.csv");
if (htmlFile) {
while (htmlFile.available()) {
client.write(htmlFile.read());
}
// close the file:
htmlFile.close();
}
client.println("</html>");
break;
}
if (c == '\n') {
currentLineIsBlank = true;
}
else if (c != '\r') { //se ricevo dal client un carriage return
currentLineIsBlank = false;
}
}
}
delay(1);
client.stop();
}
interrupts();
delay(1000);
//se è avvenuto un interrupt, quindi una basculata, vado a scrivere sulla microSD
if (blnWrite==1) {
Serial.println("il momento di scrivere");
blnWrite=false;
//scrivo su file
File dataFile = SD.open("rain.csv", FILE_WRITE);
if (dataFile) {
dataFile.println(strNow + ";0,2;mm;<br/>");
dataFile.close();
}
else {
Serial.println("errore apertura file");
}
}
}
void Basculata(){
noInterrupts();
TotPioggia=TotPioggia+0.2; //conta la pioggia
Serial.println(strNow);
Serial.println(TotPioggia);
blnWrite=true; //segnalo che è avvenuta una basculata
}Potential Derivative Project Ideas:
- Environmental Monitoring System: Integrates various environmental data such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed alongside rainfall for comprehensive monitoring.
- Agricultural Automation System: Uses rainfall data to automate irrigation systems for crops, optimizing water usage based on actual weather conditions.
- Urban Drainage System Management: Analyzes and improves the efficiency of urban drainage systems using rainfall data.
- Weather Data Sharing Platform: Develops a community or app that shares and utilizes data collected from Arduino-based rainfall sensors.
This project serves as an excellent example of how Arduino and basic electronic components can be used to create a simple yet effective weather observation tool. It is not only suitable for DIY enthusiasts but also serves educational purposes, helping to understand and utilize meteorological data effectively.