micro_ros_raspberrypi_pico_sdk
RP2040 and micro-ROS integration (USB, Wi-Fi, Ethernet)
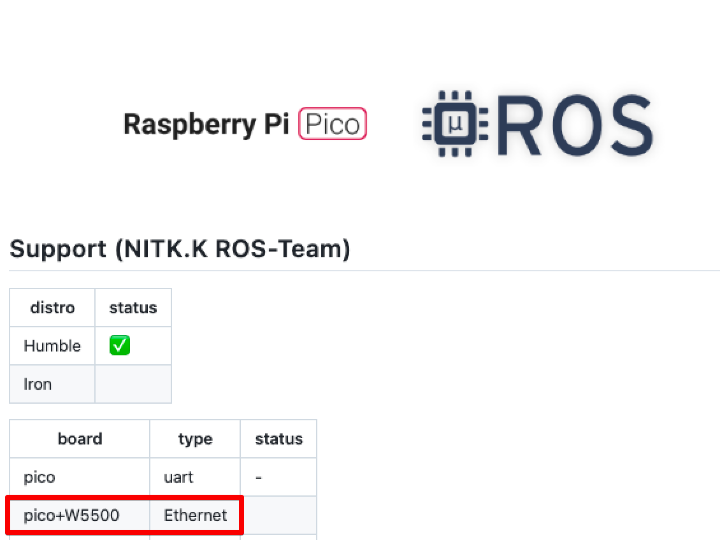
Original Project by NITKK-ROS-Team on GitHub This project is maintained by the NITKK-ROS-Team. It is a widely recognized repository in the micro-ROS community, validated by various maker projects such as Ar-Ray-code's micro_ros_pico_w_robot.
1. Introduction: What is micro-ROS?
- Definition: micro-ROS is a lightweight version of ROS 2 designed for microcontrollers (MCUs) with limited RAM and Flash. It enables these MCUs to act as first-class End-Nodes in the ROS 2 ecosystem, participating directly in the data graph via Publisher/Subscriber mechanisms.
- The Protocol: It uses DDS-XRCE (Data Distribution Service for eXtremely Resource Constrained Environments), a lightweight standard that ultimately relies on UDP/TCP transport. This is where the network performance becomes critical.
2. Market Context & WIZnet Strategy
- Current Landscape: The current micro-ROS maker market is dominated by ESP32-based Wi-Fi solutions. While convenient, they often fail to meet the stability requirements of industrial robotics.
- The Niche Opportunity: There is a clear Niche Market that demands the reliability of Ethernet over the convenience of Wi-Fi. WIZnet aims to capture this market by proving the superiority of TOE (TCP/IP Offload Engine) technology.
- Our Strategic Goals:
- Prove Performance: Demonstrate that W5500 (TOE) outperforms software stacks (LwIP) in stability and latency.
- Official Standardization: Register the W55RP20-EVB-Pico as an official micro-ROS platform board (https://micro.ros.org/).
- High-Performance Reference: Provide a reference design for a high-performance network End-Node that goes beyond simple PoC.
3. Why WIZnet? (TOE vs LwIP)
- The LwIP Bottleneck: In ESP32 or Pico W, the TCP/IP stack (LwIP) runs in software on the main MCU. This consumes significant CPU cycles and memory. More critically, heavy network traffic can interrupt the robot's control loops, causing jitter.
- The TOE Advantage: WIZnet's W5500 handles the entire TCP/IP stack in hardware.
- Offloading: The RP2040 cores are free to run complex ROS 2 logic and motor control loops.
- Stability: Hardware-based processing guarantees consistent latency, which is non-negotiable for real-time robotic control.
- W55RP20: The Ultimate Solution: The W55RP20 combines the RP2040 and W5500 into a single chip. This offers the perfect form factor for a compact, industrial-grade micro-ROS node, eliminating the need for bulky shields and complex wiring.
4. Technical Deep Dive (Code Level)
- Modular Architecture: The repository is designed for extensibility. A look at
CMakeLists.txtshows how the transport layer is isolated:
add_executable(main
main.c
interface/common/transport_common.c
interface/wifi/pico_wifi_transport.c <-- The Target
interface/uart/pico_uart_transport.c
)
- Implementation Plan: To enable W55RP20, we don't need to rewrite the core. We simply need to:
- Create
interface/ethernet/pico_ethernet_transport.c. - Implement the
uxr_custom_transportfunctions (open, close, write, read) using WIZnet's ioLibrary_Driver. - Update
CMakeLists.txtto link against the WIZnet driver instead of the Wi-Fi driver.
- Create
5. Community Validation
- Proven Reliability: This SDK is not experimental. It has been validated by Ar-Ray-code, who forked this repository to build the micro_ros_pico_w_robot. This real-world implementation proves the library's stability in mobile robotics. Adding Ethernet support to such a well-regarded library will immediately benefit a large, active user base.
- https://ar-ray.hatenablog.com/entry/2023/08/20/212113
6. How to Build (Proposed for W55RP20)
- Step-by-Step:
- Install Dependencies: Pico SDK, CMake, GCC ARM Toolchain.
- Clone Repo:
git clone https://github.com/NITKK-ROS-Team/micro_ros_raspberrypi_pico_sdk - Configure: (After our contribution) Set
PICO_BOARD=w55rp20_evb_picoin CMake. - Build:
mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make - Run Agent: Use the official Docker image:
docker run -it --rm --net=host microros/micro-ros-agent:humble udp4 --port 8888
[Korean Version]
원문 출처 (Source Mention)
Original Project by NITKK-ROS-Team on GitHub 이 프로젝트는 NITKK-ROS-Team (일본 기타큐슈 공업고등전문학교)에 의해 관리됩니다. 주목할 점은 패키지 관리자가 micro-ROS 개발사인 eProsima의 Pablo Garrido로 등록되어 있다는 것입니다. 이는 기술적 신뢰도가 매우 높으며 공식 채택될 가능성이 큼을 시사합니다. 또한 Ar-Ray-code와 같은 커뮤니티 기여자들에 의해 활발히 지원받고 있습니다.
1. 소개: micro-ROS란 무엇인가? (Introduction)
- 정의: micro-ROS는 RAM과 플래시 메모리가 제한적인 마이크로컨트롤러(MCU)를 위해 설계된 경량 ROS 2 솔루션입니다. 이를 통해 MCU가 ROS 2 생태계의 최종 노드(End-Node)로서 직접 참여하여, Publisher/Subscriber 메커니즘을 통해 데이터를 주고받을 수 있게 합니다.
- 프로토콜: ROS 2의 표준인 DDS를 경량화한 DDS-XRCE를 사용하며, 이는 궁극적으로 UDP/TCP 전송 계층에 의존합니다. 바로 이 지점에서 네트워크 성능과 안정성이 시스템 전체의 품질을 좌우하게 됩니다.
2. 시장 상황 및 위즈네트 전략 (Market Context & Strategy)
- 현재 시장: 초기 Maker 시장은 ESP32 기반의 Wi-Fi 솔루션이 주류를 이루고 있습니다. 하지만 무선 연결은 산업용 로봇이 요구하는 엄격한 안정성을 충족시키기 어렵습니다.
- 틈새 시장 (Niche Market): Wi-Fi의 불안정성을 극복하기 위해 이더넷의 신뢰성을 필요로 하는 시장이 분명히 존재합니다. 위즈네트는 TOE(TCP/IP Offload Engine) 기술의 우수성을 앞세워 이 시장을 공략하고자 합니다.
- 전략적 목표:
- 성능 입증: 범용 LwIP(소프트웨어 스택) 대비 TOE의 압도적인 성능과 안정성을 데이터로 증명합니다.
- 공식 표준화: W55RP20-EVB-Pico를 micro-ROS 공식 플랫폼 보드(https://micro.ros.org/)로 등재하여 기술 표준 위치를 확보합니다.
- 고성능 레퍼런스: 단순한 개념 증명(PoC)을 넘어, 실제 현장에서 사용 가능한 고성능 네트워크 End-Node 레퍼런스를 제공합니다.
3. 왜 WIZnet인가? (TOE vs LwIP)
로봇 제어에서는 'Real-time Stability'가 핵심
- LwIP의 병목현상: ESP32나 Pico W에서 사용하는 소프트웨어 TCP/IP 스택(LwIP)은 메인 MCU의 자원을 상당히 소모합니다. 특히 네트워크 트래픽이 몰릴 경우, CPU가 패킷 처리에 매달리느라 로봇의 제어 루프를 방해하여 지터(Jitter)를 유발할 수 있습니다.
- TOE의 우위: 위즈네트의 W5500은 TCP/IP 스택 전체를 하드웨어로 처리합니다.
- 오프로딩 (Offloading): RP2040 코어는 네트워크 처리 부담에서 완전히 해방되어, 오직 애플리케이션 로직에만 집중할 수 있습니다.
- 안정성: 하드웨어 기반 처리는 일정한 지연 시간(Deterministic Latency)을 보장하며, 이는 실시간 제어에 필수적입니다.
- W55RP20: 궁극의 솔루션: W55RP20은 RP2040과 W5500을 단일 칩으로 통합했습니다. 이는 복잡한 배선이나 부피 큰 쉴드 없이도, 가장 컴팩트하고 강력한 산업용 micro-ROS 노드를 구현할 수 있게 해줍니다.
4. 기술적 심층 분석 (Technical Deep Dive)
- 모듈화된 아키텍처: 이 리포지토리는 확장성을 고려해 설계되었습니다.
CMakeLists.txt를 보면 전송 계층이 어떻게 격리되어 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다:
- 구현 계획: W55RP20을 지원하기 위해 코어 로직을 뜯어고칠 필요가 없습니다. 우리는 단지 다음 단계만 수행하면 됩니다:
interface/ethernet/pico_ethernet_transport.c파일을 생성합니다.- WIZnet ioLibrary_Driver를 사용하여
uxr_custom_transport함수들(open, close, write, read)을 구현합니다. CMakeLists.txt에서 Wi-Fi 드라이버 대신 WIZnet 드라이버를 링크하도록 수정합니다.
5. 커뮤니티 검증 (Community Validation)
- 입증된 신뢰성: 이 SDK는 실험적인 코드가 아닙니다. Ar-Ray-code가 이 리포지토리를 포크하여 micro_ros_pico_w_robot을 제작함으로써 그 안정성을 입증했습니다. 이러한 실제 구현 사례는 모바일 로보틱스 분야에서의 라이브러리 신뢰성을 증명합니다. 이렇게 검증된 라이브러리에 이더넷 지원을 추가하는 것은 거대한 잠재 사용자층에게 즉각적인 혜택을 줄 것입니다.
- https://ar-ray.hatenablog.com/entry/2023/08/20/212113
6. 빌드 방법 (W55RP20 제안)
- 단계별 가이드:
- 의존성 설치: Pico SDK, CMake, GCC ARM Toolchain.
- 리포지토리 복제:
git clone https://github.com/NITKK-ROS-Team/micro_ros_raspberrypi_pico_sdk - 설정: (기여 완료 후) CMake에서
PICO_BOARD=w55rp20_evb_pico설정. - 빌드:
mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make - 에이전트 실행: 공식 도커 이미지 사용:
docker run -it --rm --net=host microros/micro-ros-agent:humble udp4 --port 8888
DOCUMENTS (문서 및 자료)
- Code: https://github.com/NITKK-ROS-Team/micro_ros_raspberrypi_pico_sdk
- Community Reference: https://github.com/Ar-Ray-code/micro_ros_pico_w_robot (Validated by Ar-Ray-code)
- Official Docs: https://micro.ros.org/
