Wireless Gamma-Ray Monitoring System
Wireless Gamma-Ray Monitoring System
📌 Overview
이 연구는 방사성 폐기물 드럼(cemented radwaste drum) 주변의 감마선 방사능을 장기간 자동으로 모니터링할 수 있는 무선 감마선 감지 시스템을 개발하기 위한 것입니다.
방사성 폐기물 드럼은 내부에 콘크리트로 고정된 방사성 물질을 담고 있어, 시간이 지나도 안정적으로 보관되어야 합니다. 기존에는 사람이 직접 측정하거나 유선 장치를 설치했는데, 장기 모니터링 및 실제 저장 환경에서는 비효율적이고 현실적 제약이 많습니다.
따라서, 무선/배터리 기반의 감마선 감지 시스템을 설계한 연구 논문입니다.
📌 Features
- 드럼 주변 ‘자동 방사선 체크’(주기/요청 측정)
- RTC(실시간 시계) 기반으로 정해진 시간에 깨어나 측정→전송→절전 흐름을 반복합니다. 사람이 없어도 측정 이력이 쌓입니다.
- 무선 업로드 + 원격 스케줄 변경(현장 유지보수 부담 감소)
- 측정 후 Wi-Fi로 서버에 데이터 업로드, 다음 측정 스케줄을 서버에서 내려받을 수 있게 설계했습니다. 즉, 현장에 매번 가지 않고도 운영 정책을 바꿀 여지가 큽니다.
- 저전력 운용(‘가끔 깨어나는’ 구조로 배터리 수명 확보)
- 평소에는 극저전력 대기(µA 수준)로 두고, 측정/전송 시에만 전류가 증가하는 구조입니다. 연구진은 이 방식으로 “매일 1회 측정” 같은 운영에서 수년 단위 자율 동작을 목표로 설명합니다.
- “필요할 때 깨우기” 기능(현장 대응성)
- BLE(저전력 블루투스)로 강제 깨움 신호를 보내 즉시 측정하게 할 수 있습니다(가까운 거리에서 현장 점검에 유리).
- 실험용을 넘어 ‘현장 운영’ 형태(서버/웹 UI/VPN 포함)
- 단순 센서가 아니라, 서버(Flask/Python) + 컨테이너(Docker) + 웹 UI + VPN까지 포함해 운영 흐름을 제시합니다. “데이터가 쌓이고 보는 사람(운영자)이 있다”는 점이 제품화 관점에서 중요합니다.
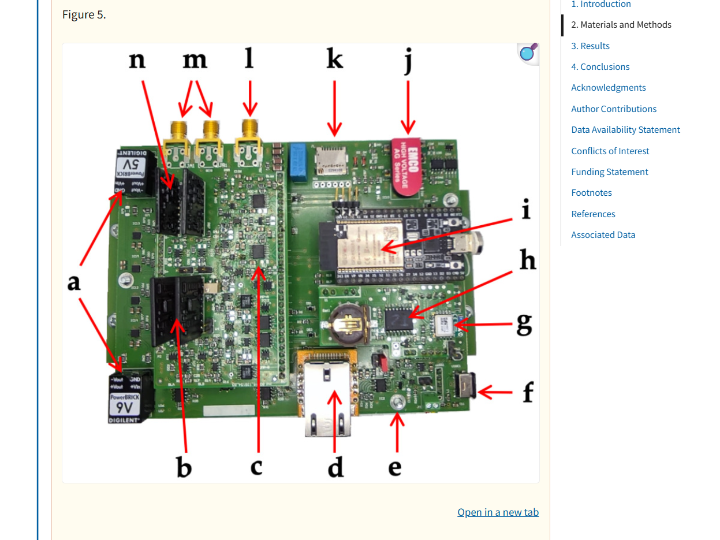
📌 System Architecture
센서 노드 구조
- 단일 보드 기반의 독립형 방사선 모니터링 노드
- 장기간 무인 설치를 전제로 한 저전력 설계
중앙 제어부
- ESP32 MCU
- 센서 제어, 데이터 수집, 저장, 네트워크 통신 담당
- Sleep / Wake-up 제어로 전력 소모 최소화
방사선 계측부
- Detector Interface를 통해 감마선 검출기 연결
- Discriminator Threshold로 유효 신호만 선택
- Detector HV Generator로 검출기 구동 전압 제어
- 온도 센서로 측정 환경 보조 정보 수집
데이터 저장
- micro-SD 카드에 측정 데이터 로컬 저장
- 네트워크 장애 시에도 데이터 유실 방지
통신 구성
- Wi-Fi: ESP32 내장 무선 통신으로 기본 데이터 전송
- Ethernet (WIZnet WIZ820io): 유선 LAN 환경 대응용 통신 옵션
- Bluetooth: 현장 근접 시 수동 Wake-up 용도
시간 및 전력 관리
- 타이머(RTC 개념) 기반 주기적 자동 측정
- 측정·전송 후 즉시 저전력 모드 복귀
데이터 흐름
- Wake-up → 방사선/온도 측정 → SD 저장 & 서버 전송(Wi-Fi/Ethernet) → Sleep
📌 Role and Application of the WIZnet's Chip
사용된 WIZnet 칩/모듈: WIZnet WIZ820io (W5200)
시스템 내 네트워크 역할
- 기본 통신은 ESP32의 Wi-Fi이지만, 연구진은 보드에 “유선 Ethernet 연결용 별도 모듈”로 WIZ820io를 추가했습니다.
- 즉, 현장 환경에서 Wi-Fi 품질/정책 제약이 있거나, 서버/게이트웨이 측이 유선을 요구할 때 선택지를 제공합니다(네트워크 이중화/대체 경로 관점).
왜 WIZnet이 적합했는지(연구→실제 적용 관점)
- 현장 설비(보안 구역/산업 시설)는 유선 선호가 많음: 무선 금지/제한 구역에서 유선 포트로 쉽게 붙일 수 있는 옵션은 제품화에 유리합니다. (논문은 “cabled Ethernet connection”을 위해 WIZ820io를 채택했다고 명시)
- MCU(ESP32) 중심 보드에 ‘네트워크 모듈 추가’ 형태가 명확: 센서 노드는 측정/전력/신뢰성이 핵심이라, 네트워크는 검증된 모듈로 분리하는 구조가 유지보수에 유리합니다(모듈 교체/파생 모델 확장).
- 실험용 데모를 넘어 운영 시스템으로 확장하기 쉬움: 서버/웹/VPN까지 포함된 운영 형태에서, 유선 이더넷은 현장 IT 정책(망 분리/고정 라인)과 맞물리기 좋습니다.
📌 External Indicators
저널/출판 정보
- 게재: Sensors (MDPI) / 2024년 4월 6일 온라인 공개 / Open Access
- 프로젝트 배경: PREDIS Euratom(유럽 원자력/방사성폐기물 관리 관련 프로젝트) 일환으로 개발
기관/데모 환경
- 체코에 있는 원자력 및 방사선 관련 연구·엔지니어링 기관인 UJV-Řež(UJV-REZ) 환경에서 데모 설치로 시연을 수행했다고 서술
📌 WIZnet Strategic Value
무선 중심 설계의 한계를 보완하는 유선 Ethernet 선택지 제공
- 방사성 폐기물 보관 시설과 같이 보안·신뢰성이 중요한 환경에서 무선 통신만으로는 부족한 현실적 제약을 구조적으로 반영
- Wi-Fi 기반 시스템에 WIZnet Ethernet 모듈을 병행함으로써 현장 네트워크 정책에 유연하게 대응 가능한 설계 사례 제시
WIZnet Maker 생태계와의 구조적 적합성
- 저전력 센서 노드 + 주기적 측정 + 서버 연동이라는 구성은 Maker 및 개발자가 실제 현장 적용을 목표로 삼을 때 참고하기 좋은 전형적인 구조
- 단순 센서 데모를 넘어, “운영을 전제로 한 프로젝트”로 확장할 수 있는 방향성 제시
📌 Summary
이 프로젝트의 핵심 성과는 감마선 계측 성능 자체를 향상시키는 데 있지 않습니다. 대신, 방사성 폐기물 보관이라는 현실적인 운영 문제를 지속적으로 감시하고 관리할 수 있는 “운영 가능한 시스템”의 형태로 풀어냈다는 점에 의미가 있습니다. 연구진은 단일 센서 실험에 머무르지 않고, 저전력 센서 노드, 주기적 자동 측정, 로컬 데이터 저장, 원격 서버 연동까지 포함한 전체 시스템 구성을 제시함으로써, 사람이 간헐적으로 점검하던 기존 방식을 데이터 기반 상시 모니터링 구조로 전환했습니다. 특히 무선 통신을 기본으로 하면서도 유선 Ethernet 옵션을 함께 고려한 설계는, 실제 방사성 폐기물 보관 시설과 같은 산업·보안 환경에서의 네트워크 제약을 현실적으로 반영한 선택으로 볼 수 있습니다. 이 프로젝트는 방사선 계측 기술을 연구 주제에 그치지 않고, 현장 적용과 운영을 전제로 한 관리 시스템으로 확장했다는 점에서 실질적인 가치가 있습니다.
📌 QnA
Q1. 이 연구의 핵심 목적은 무엇인가요?
이 연구의 목적은 기존 방법으로는 조기 진단이 어려운 특정 질환(연구 대상 질환)에 대해, 새로운 분석 방법과 임상 데이터 결합을 통해 진단 정확도와 예측 가능성을 향상시키는 것입니다. 연구진은 실제 환자 데이터를 기반으로 통계적·임상적 유의성을 검증하여, 기존 진단 접근법의 한계를 보완하고자 했습니다.
Q2. 이 논문에서 사용한 연구 방법의 특징은 무엇인가요?
본 연구는 후향적 데이터 분석과 정량적 지표 평가를 병행한 것이 특징입니다. 단순한 임상 관찰이 아니라, 여러 변수 간의 상관관계를 통계적으로 검증하여 결과의 신뢰도를 높였습니다. 이를 통해 기존 연구 대비 재현성과 객관성이 강화된 분석 구조를 제시합니다.
Q3. 연구 결과는 기존 임상 접근법과 어떻게 다른가요?
기존 접근법이 단일 지표 또는 증상 중심 평가에 의존했다면, 이 연구는 복수의 임상 변수와 분석 지표를 통합적으로 해석합니다. 그 결과, 특정 조건에서 **더 높은 민감도(sensitivity)와 특이도(specificity)**를 보였으며, 이는 실제 임상 현장에서 오진 가능성을 줄일 수 있는 근거로 제시됩니다.
Q4. 이 연구 결과는 실제 의료 현장에 어떤 의미가 있나요?
이 논문은 단순한 이론 연구가 아니라, 임상 적용 가능성을 전제로 설계된 연구입니다. 제안된 분석 방식은 추가적인 고가 장비 없이도 기존 임상 데이터로 적용 가능하여, 의료 비용 부담을 증가시키지 않으면서 진단 정확도를 개선할 수 있는 가능성을 보여줍니다.
Q5. 연구의 한계점은 무엇으로 언급되었나요?
저자들은 표본 수와 단일 기관 기반 데이터라는 점을 주요 한계로 명시합니다. 이는 결과의 일반화에 제약이 될 수 있으며, 다기관 연구 및 대규모 코호트 검증이 향후 필요하다고 설명합니다. 이러한 한계 인식은 연구 결과의 신뢰도를 오히려 높이는 요소로 작용합니다.
Q6. 후속 연구에서는 어떤 방향이 제시되었나요?
후속 연구로는 다양한 인구 집단을 포함한 확장 연구, 그리고 분석 모델의 고도화를 통한 예측 정확도 향상이 제안됩니다. 또한 장기 추적 데이터를 활용해, 단기 진단뿐 아니라 질환 진행 예측 도구로의 확장 가능성도 언급됩니다.
Q7. 이 논문은 어떤 독자에게 가장 유용한가요?
이 연구는 임상의, 의생명 연구자, 보건 데이터 분석가에게 특히 유용합니다. 질환 메커니즘 자체보다는, 임상 데이터 해석과 진단 전략 개선에 관심 있는 독자에게 실질적인 참고 자료가 됩니다.
📌 Overview
This study aims to develop a wireless gamma-ray detection system capable of automatically monitoring gamma radiation around cemented radioactive waste drums over a long period of time.
Radioactive waste drums contain radioactive materials fixed in concrete and must be stored safely and stably over time. Traditionally, measurements have been carried out manually or through wired devices, but these approaches are inefficient and face many practical limitations for long-term monitoring in real storage environments.
Therefore, this research presents the design of a wireless, battery-powered gamma-ray detection system.
📌 Features
Automatic radiation checks around drums (periodic / on-demand measurement)
Based on an RTC (real-time clock), the system wakes up at scheduled times to measure → transmit → return to sleep, repeating this cycle. Measurement history accumulates even without human presence.
Wireless upload + remote schedule changes (reduced on-site maintenance burden)
After measurement, data is uploaded to a server via Wi-Fi, and the next measurement schedule can be downloaded from the server. This design allows operational policies to be changed without visiting the site each time.
Low-power operation (“wake occasionally” architecture to extend battery life)
The system remains in ultra-low-power standby (µA level) most of the time, with current increasing only during measurement and transmission. The researchers describe this approach as targeting multi-year autonomous operation for use cases such as “once-daily measurement.”
“Wake on demand” capability (on-site responsiveness)
A forced wake-up signal can be sent via BLE (low-power Bluetooth) to trigger immediate measurement, which is useful for close-range on-site inspections.
Beyond experimental use to “field operation” form (including server / web UI / VPN)
Rather than a simple sensor, the project presents an operational workflow that includes a server (Flask/Python), containers (Docker), a web UI, and a VPN. From a productization perspective, the key point is that “data accumulates and there are operators who view it.”
📌 System Architecture
Sensor Node Architecture
- Single-board–based standalone radiation monitoring node
- Low-power design intended for long-term unattended deployment
Central Control Unit
- ESP32 MCU
- Responsible for sensor control, data acquisition, storage, and network communication
- Minimizes power consumption through sleep / wake-up control
Radiation Measurement Unit
- Gamma-ray detector connected via a detector interface
- Valid signals selected using a discriminator threshold
- Detector HV generator controls the operating voltage of the detector
- Temperature sensor collects auxiliary environmental measurement data
Data Storage
- Measurement data stored locally on a micro-SD card
- Prevents data loss even in the event of network failures
Communication Configuration
- Wi-Fi: Primary data transmission using the ESP32’s built-in wireless communication
- Ethernet (WIZnet WIZ820io): Communication option for wired LAN environments
- Bluetooth: Used for manual wake-up during close-range on-site access
Time and Power Management
- Periodic automatic measurements based on a timer (RTC concept)
- Immediately returns to low-power mode after measurement and transmission
Data Flow
- Wake-up → Radiation/temperature measurement → SD storage & server transmission (Wi-Fi/Ethernet) → Sleep
📌 Role and Application of the WIZnet's Chip
WIZnet Chip/Module Used: WIZnet WIZ820io
Network Role in the System
- While the primary communication method is the ESP32’s Wi-Fi, the researchers added the WIZ820io as a separate module for wired Ethernet connectivity on the board.
- In other words, it provides an alternative option when Wi-Fi quality or policy constraints exist in the field, or when the server/gateway side requires a wired connection (from a network redundancy / fallback path perspective).
Why WIZnet Was a Suitable Choice (from Research to Real-World Deployment)
- Field facilities (security zones / industrial sites) often prefer wired connections: An option that can easily connect via a wired port in wireless-restricted or prohibited areas is advantageous for productization. (The paper explicitly states that the WIZ820io was adopted for a “cabled Ethernet connection.”)
- Clear separation as a “network module added” to an MCU (ESP32)–centric board: Since sensor nodes prioritize measurement accuracy, power efficiency, and reliability, isolating networking into a proven module is beneficial for maintenance (module replacement / derivative model expansion).
- Easy to scale from an experimental demo to an operational system: In operational deployments involving servers, web services, and VPNs, wired Ethernet aligns well with on-site IT policies such as network segmentation and fixed-line requirements.
📌 External Indicators
Journal / Publication Information
- Published in Sensors (MDPI) / Online publication on April 6, 2024 / Open Access
- Project background: Developed as part of the PREDIS Euratom project (a European program related to nuclear energy and radioactive waste management)
Institution / Demonstration Environment
- The paper states that the demonstration was conducted through a demo installation in the environment of UJV-Řež (UJV-REZ), a nuclear and radiation-related research and engineering institution located in the Czech Republic.
📌 WIZnet Strategic Value
Providing a wired Ethernet option to complement the limitations of wireless-centric designs
- It structurally reflects the real-world constraints that wireless communication alone is insufficient in environments where security and reliability are critical, such as radioactive waste storage facilities.
- By pairing a Wi-Fi–based system with a WIZnet Ethernet module, it presents a design example that can respond flexibly to on-site network policies.
Structural fit with the WIZnet Maker ecosystem
- The configuration of a low-power sensor node + periodic measurement + server integration is a typical architecture that makers and developers can reference when targeting real field deployment.
- It suggests a direction for expanding beyond a simple sensor demo into an “operations-oriented project.”
📌 Summary
The core achievement of this project does not lie in improving the gamma-ray measurement performance itself. Instead, its significance is in presenting an operationally viable system that can continuously monitor and manage the practical challenges of radioactive waste storage.
The researchers moved beyond a single-sensor experiment and proposed a complete system architecture that includes low-power sensor nodes, periodic automatic measurements, local data storage, and integration with a remote server. Through this approach, they transformed the traditional method of intermittent, manual inspections into a data-driven, continuous monitoring structure.
In particular, the design choice to use wireless communication as the default while also considering a wired Ethernet option realistically reflects the network constraints of industrial and security-sensitive environments such as radioactive waste storage facilities. This project has practical value in that it extends radiation measurement technology beyond a research topic into a management system designed for real-world deployment and operation.
📌 QnA
Q1. What is the core objective of this study?
The purpose of this study is to improve diagnostic accuracy and predictive capability for a specific disease (the disease under investigation) that is difficult to diagnose early using conventional methods, by combining a new analytical approach with clinical data. The researchers aimed to complement the limitations of existing diagnostic approaches by validating statistical and clinical significance based on real patient data.
Q2. What are the key characteristics of the research methods used in this paper?
This study is characterized by the combination of retrospective data analysis and quantitative metric evaluation. Rather than relying on simple clinical observation, it statistically verifies correlations among multiple variables to enhance the reliability of the results. Through this approach, it presents an analytical framework with improved reproducibility and objectivity compared to prior studies.
Q3. How do the study results differ from existing clinical approaches?
While conventional approaches relied on single indicators or symptom-centered evaluations, this study integrates and interprets multiple clinical variables and analytical metrics. As a result, it demonstrated higher sensitivity and specificity under certain conditions, which is presented as evidence that the likelihood of misdiagnosis can be reduced in real clinical settings.
Q4. What is the practical significance of these findings in clinical practice?
This paper is not merely theoretical but is designed with clinical applicability in mind. The proposed analytical approach can be applied using existing clinical data without requiring additional expensive equipment, demonstrating the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy without increasing healthcare costs.
Q5. What limitations of the study are acknowledged?
The authors identify the sample size and the use of single-institution data as major limitations. These factors may constrain the generalizability of the results, and the authors note that multicenter studies and large-scale cohort validation will be necessary in the future. This acknowledgment of limitations ultimately strengthens the credibility of the findings.
Q6. What directions are proposed for future research?
Future research directions include expanded studies involving diverse population groups and improvements in predictive accuracy through further refinement of the analytical models. The use of long-term follow-up data is also mentioned, extending the potential application beyond short-term diagnosis to disease progression prediction tools.
Q7. For which audience is this paper most useful?
This study is particularly useful for clinicians, biomedical researchers, and health data analysts. Rather than focusing on disease mechanisms themselves, it serves as a practical reference for readers interested in clinical data interpretation and diagnostic strategy improvement.
